
Science Based
CosmologyGlossary of Cosmology Principles
"If it disagrees with experiment, its wrong." - Physics Nobel Prize winner Richard Feynman
Science Based Cosmology is limited to ideas meeting the minimum criteria for a scientific claim.
This set of Cosmology principles definitions is possibly the web’s most complete, explicit and accurate glossary from a physics point of view. It is the most complete (and rare) because it presents the best evidence and reasoning from both sides of the Big Bang controversy. It is explicit in explaining definitions of cosmology terms in the least ambiguous way possible without losing any accuracy. You will also find abundant high-quality references for controversial topics linked in.
Although written at a Scientific American reading level intended for astrophysicists, cosmology students and scientists from other disciplines, it should be useful and understandable for anyone with a passion for science, particularly student astronomers and enthusiasts. Even so, an experienced cosmologist might learn a useful new principle or two here. (Are you aware there are more than 600 galaxies exhibiting Blueshift? Are you familiar with Malmquist bias or the Joule-Kelvin Effect?)
No math expertise is needed and no equations are employed (but a sense of humor might help in appreciating my occasional diversions). You also won't need to know what scalars, vectors or tensors are, or how to use them. To help you research further, this glossary is abundantly referenced with web links.
Caution: Please bear in mind that almost every idea and interpretation in cosmology (not astrophysics) is disputed; every idea from the Age of our Universe, through Expansion, Microwave Background, Galaxy Rotation meaning Dark Matter, Inflation, Supernovae indicating Dark Energy, to Tired-Light and Spectral line Redshift. Observations are rarely contested, but the interpretation of the data is. This conclusion is based on my decades of research leading to this 15,000 word glossary. The disputes use generally rational arguments by generally reasonable people from the many different sides of the debate. I try to present the best available evidence and reasoning here (and provide the best available science links for further research) so you can make up your own mind.
If you dispute Professor Feynman's concise threshold -- "If it disagrees with experiment, its wrong" - then you might prefer a website on Astrology. Ungrounded flights of fancy are fine for novels and Hollywood, but I do not have much patience for them when used as claims of scientific fact - even when provided by highly credentialed Theoreticians. Which is why you will also find definitions of key logical fallacies and cognitive biases almost certainly bearing on cosmology.
Disclaimer: I do have a bias. My bias is to trust only physical experiments that provide actual observable results and explanations that do not commit a logical fallacy or violate a law of physics. Please don't confuse my effort to provide you with the best available explanations of Cosmology ideas with my suggesting that all of the following concepts are consistent with solidly established laws of physics, are free of logical fallacies or valid. More than a few cosmology concepts are logically contradictory, meaning they can't all be true.
Cosmology is terrifically exciting. It is thrilling for me to examine the Hubble 2012 Extreme Deep Field photographs and the 3-D maps of the spectacularly giant galaxy sheets and filaments. This glossary was made to help you enjoy cosmology more by understanding the ideas about what is going on. It provides you with the leading concepts of how everything works and lets you know where we don't have good answers - yet. I hope the glossary is helpful for you to enjoy this fascinating field and maybe you can contribute to better understanding our Universe's largest scale dynamics.
"With miracles, any sort of evidence will do, but facts require proof." - Mark Twain
| Home | Overview | Blog | Glossary of Cosmological Principles | References | News |
Age, Universe
Older than Cher, younger than Mick Jagger. ( ;-) (1)
Astrophysicists have wildly divergent claims of Universe age depending on which model they embrace: from about 14 billion to a trillion years old, to infinite in age.
Big Bang supporters claim the Universe age is exquisitely precisely calculated by Planck 2013 microwave data, based on a Lambda-Cold Dark Matter model, at 13.8 billion years (plus or minus a few million years - unless you are running a bit late for tea.) . (Since far more reliable distance ladder steps, such as Parallax, are no more accurate than 10 percent, that age claim may invoke a logical fallacy called False Precision.) This age conflicts with the age of a nearby star (HD 140283) that seems to be easily almost 10 percent older, at least 14.5 Billion years old.
Other Cosmologists support cosmological models maintaining that our Universe is at least a Trillion years old to infinite in age.
There is no good (credible and persuasive) answer or explanation of how things got started or what conditions were like "before" a purported start.
Astrophysics includes the study of all natural phenomena outside Earth's atmosphere including physics at the nuclear, atomic and molecular scales. Cosmology is a subset of Astrophysics which generally excludes study of phenomena smaller than solar systems, but in the 1990s greatly expanded studies of physics at the nuclear, atomic and molecular scales.
(No evidence)
An ambiguously defined set of claims that the movements of planets among stars significantly affect individual human activities. There are at least three kinds of astrology including Vedic, Mayan, Chinese. Some astrology claims have been tested, but none have shown any evidence of efficacy, predictability or repeatability.
A set of complex conjectures
that there is a measuring stick arising from conjectured Pressure-Density waves in the baryon-photon (matter-radiation) fluid for the first 300,000
years after Big Bang.
The idea goes like this : At about 300,000 years, photons and matter permanently separated, never to interact again. (Please remember - I'm just reporting this.)
(The term "acoustic" is misleading as there is no Sound physics involved.)
(This claim has no meaning outside Big Bang / Expansion models.)
The most well known cosmology model, "Big Bang" refers to not one idea, but an assortment of a few dozen controversial cosmology models or conjectures based on an Expanding Universe idea where gravity dominates the largest scale Universe dynamics rather than electromagnetic effects and plasma. These are often collectively called the "Standard Model" or "Standard Cosmology."
I find it notable that the International Astronomical Union (IAU) does not provide a definition of, or support for, any Big Bang model. My research shows there is no definitive definition of Big Bang and my 2009 paper suggests that some astronomical body should take that responsibility. Until that occurs, let me offer the following definition of Big Bang distilled from the best available information.
All Big Bang models generally propose that all the matter, energy, forces and space of today's Universe was created instantaneously from a hot dot smaller than an electron some 14 billion years ago and expanded (not exploded) and cooled to what we now experience.
All the leading Big Bang models are ambiguous (a potentially fatal logical fallacy), lack fully defined fundamental terms, require up to half a dozen or more adjustable parameters, require undetected matter, forces, energy and phenomena, and have unstable claims or definitions (sometimes charitably called "dynamic" or "moving goal posts").
There is no single agreed upon Big Bang model. Some of the better known of the several dozen Big Bang models are Lambda-Cold Dark Matter, "Relativistic Friedman-LeMaitre" (open and closed versions), McGaugh, Einstein-deSitter relativistic, LeMaitre, Eddington-LeMaitre, and Zero-Kelvin.
The various Big Bang models have several optional amendments including Inflation and acceleration.
Big Bang's Expansion is a mathematical model (called FLRW) derived from (it is a solution to) General Relativity's field equations. It is dependent upon two assumptions: that our Universe is extremely uniform; specifically homogenous and isotropic.
Model - Not a Theory: It is not widely understood that Big Bang is not yet a theory or a hypothesis. It is notable that the most cited author of Big Bang concepts, Princeton's P. James E. Peebles, does not refer to the "Big Bang" as a "theory," he accurately calls it a "model."(2)
"It is sensible and prudent that people should continue to think about alternatives to the standard model [Big Bang], because the evidence is not all that abundant."
So despite the fact that a web search will return more than 9 million results for the term - there is no Big Bang "Theory" in astrophysics, at least not yet. However, there are several dozen Big Bang "Models."
Big Bang models have at least 6 to as many as 19 adjustable parameters.
Many popular authors, and even a few scientists who should know better, overlook this vital and enormous distinction. Any astrophysicist calling Big Bang a "theory", is either unaware of, has forgotten, or is deliberately ignoring the dramatic and important difference between a model and the bare minimum for a scientific hypothesis.
Components: The various Big Bang models are based upon and require some seven interdependent ideas, including at least three conjectures -
- the hypothesis that there is a Spectral line Redshift-to-Distance correlation - which is observed, though it does have a large variance or margin of error,
- the hypothesis that the Redshift-to-Distance correlation also means that most galaxies are rushing away from us at Recession Velocity,
- the conjecture that Recession Velocity implying our Universe (other than galaxies) is stretching called "Universe Expansion,"
- Universe Expansion requires not the well known and studied Doppler Effect but, a conjectured Relativistic Doppler Effect,
- the conjecture that we can extrapolate the purported Universe Expansion backward in time 14 billion years to a moment when all the matter and energy in our Universe were packed together in a volume smaller than an electron.
- the conjectured Cosmological Constant-Vacuum Fluctuations which are constantly creating matter from nothing, and which are only explained by and need --
- The hypothetical Higgs Field and its Higgs Boson.
Big Bang models also require --
Evidence: Even though Big Bang is not yet a scientific claim where evidence is relevant, its supporters point to interpretations of observations including Redshift (the spectral line redshift distance correlation interpreted as meaning Universe expansion), Cosmic Microwave Radiation (that we are bathed in microwave radiation from our Universe's "background" that originated soon after Big Bang), Nucleosysthesis (that the amounts and ratios of light element isotopes can only mean they were all created at one moment), Supernova 1A decay taking longer at large distances implying our Universe is stretching, distant galaxies appearing younger than nearby galaxies, and Olber's (or Cheseaux's) Paradox.
As of March 2013, Big Bang theorists admit that according to their conjectures -- ~ 95 percent of our Universe's matter, energy, forces and space is either undetected, unexplained or unknown while known matter only composes 4.9 percent of the total.
Controversial: Big Bang / expansion models are so controversial they have spawned abundant, solid, highly informed dispute in science-based astrophysics papers, books, and Conferences. This led to the formation of a growing worldwide organization of astrophysicists and the eminent Open Letter of concern signed by hundreds of astrophysicists, astronomers, and scientists and published in NewScientist.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#BigBang
(The Big Bang set of conjectures are accurately described as a moving target. These amendments are intended to solve a few of Big Bang's problems.)
1) Inflation Conjectures (no evidence)
Inflation conjectures amend Big Bang, by claiming that the conjectured Universe Expansion underwent an astounding acceleration (magnitudes greater than light speed), and then slowed down to essentially zero (22 millimeters per second / light-year) all within the very first second. The authors propose that this was caused by gravity reversing its force due to a False Vacuum. This stretching is supposed to smooth out all wrinkles in the initial lumpiness.
The conjectures are intended to solve some of Big Bang's generally accepted problems including - Horizon, Smoothness, Flatness, Magnetic monopoles and arbitrary initial conditions.
There are now at least half a dozen very different Inflation conjectures (Old Inflation, New Inflation, Chaotic, Stochastic, Modified Gravity or "Eternal" Inflation, Hybrid, Supersymetric, etc.) none of which are widely supported. One early (1981) concept claims the Universe doubled in size every 1030 of a second for some 100 doublings; growing from smaller than atomic size to a ball that would encompass our nearest 20 galaxies in less than a second.
No version of Inflation provides an explanation for either the proposed acceleration or slowing using any kind of physics we can test in a laboratory or physical forces as we know them. In fact, the slowing is rarely discussed at all. The only explanation offered is a mythical "Inflaton field" or a decay of the False Vacuum. Incidentally, while the Inflation is supposed to have begun and remains wholly uniform through this gigantic dynamic change, apparently it doesn't end uniformly; there are some spots that continue inflating after everything else has quit.
Update July 2012: Doubt about Inflation is now widespread. "Inflation has destroyed itself. It logically self-destructed." - Max Tegmark, MIT 2012
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Inflation
The Accelerating Universe conjecture amends Big Bang models by claiming the Universe is not merely expanding or stretching, but that the purported expansion has recently (~6 billion years ago) started accelerating. This concept is an interpretation of 1998 observations that claim distant supernova appear dimmer at maximum brightness than expected.
Accelerating Universe is a three part conjecture:
- Because some nearby supernova (at intermediate redshifts) appear about 25% dimmer than expected at maximum brightness some interpret this as meaning that the supernova are farther away than expected.
- They then interpret the unexpected farther - ness as meaning that "something" extra pushed them.
- Their first choice for that "something" extra is a conjectured new force that is repulsive to gravity.
Critics point out that:
- Measurements of the brightest galaxies in similarly distant clusters show no similar dimming (Tom Andrews, 2009).
- When corrected for
Malmquist bias there is no Supernova dimming (which means as you see further from Earth, only the brightest examples of phenomena are visible, biasing conclusions to a subset of the whole phenomena).- In addition, if acceleration is occurring, then doesn't that mean some force other than gravity is dominating our universe? Theorists are now claiming Yes, that the never detected "
Dark Energy" is now the predominant force.
An idealized or reference perfect absorber of radiation useful for understanding the physics of thermal equilibrium. Such a theoretical object emits a predictable temperature-dependent radiation spectrum. The textbook example is a box with a tiny hole in the side.
There is no strictly exact blackbody in nature, but good approximations are provided by individual stars and a closed graphite box at a steady temperature.
However, the microwave "background" radiation hypothesis claims to provide a "perfect" thermal emission spectrum to a blackbody.
A hypothetical "object" or region of physical space where gravity is so strong it prevents any matter from escaping and even light cannot escape.
Critics say that as defined, a Black Hole is impossible to create. They prefer the idea that the intense gravity objects are Neutron stars.
While the hypothesis itself means a black hole is inherently invisible or unobservable directly, there is powerful new evidence of several stars orbiting an invisible region at the center of our galaxy that is hard to explain as something other than phenomena visibly acting as a Black hole or Neutron star would.
To see stars orbiting a powerful invisible attraction force at the center of our galaxy and make abrupt turns, click on the image below.
Graphic courtesy W. M. Keck Observatory / UCLA Galactic Center Group
Compact energy star/source at galaxy centers, with high amounts of X-ray radiation, and jets of matter ejected at near, and sometimes seemingly many times faster than (superluminal), the speed of light. These jets can exhibit Blueshift.
Huge volumes of gas and plasma as large as 400,000 light years across (4 times the diameter of our Milky Way galaxy).
Terms used to communicate the energy radiated by astrophysical objects.
Flux, Energy
Fluence
Bolometric Luminosity
Apparent Luminosity
Magnitude
Magnitude, Absolute
Distance Modulus
Standard Candle
Photon Velocity
Cosmological Brightness DimmingDo note that some terms are limited to visible light, while others include energy from the entire electromagnetic spectrum from gamma rays through radio waves.(Analogies with water in a hose are in parentheses.)
Luminosity and Brightness are independent of the Frequency and Wavelength of photons. (The "temperature" of water in a hose is a poor analogy as temperature is independent of brightness, and radiation does not have a temperature.)
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Bright
Energy Flux: Photon energy per unit area (rate of water flowing through a hose). Sun's Flux ~ 1,367 watts / square meter at Earth's surface (on a sunny day near the Equator).
Fluence = Flux x Time: Energy / unit area over an amount of time, e.g. kilowatt hours. (Or the amount of water needed to fill a glass or a swimming pool.)
Bolometric Luminosity: Total radiant energy from a source, from shortest to longest wavelengths, from gamma-rays to radiowaves. Brightness of an astronomical object totaling all energy across the entire electromagnetic spectrum, independent of distance.
Apparent Luminosity means only visible light - not other radiation wavelengths (outside ~360 to ~830 nanometers; there are one million nanometers in a millimeter). Both are measured as absolute magnitude, measured in watts, or Joules, or by using our Sun's brightness as 1.0 on the Solar scale.
- Luminosity measures what is emitted.
- Brightness measures what is received.
- Brightness decreases as distance increases.
- Luminosity remains steady as distance increases. However, luminosity is extremely sensitive to changing temperature of the star. Double the temperature of a star and it radiates 16 times more luminosity.
Magnitude: Relative brightness of an astronomical object measured in a specific wavelength or passband, usually in visible light range, using a logarithmic scale. Used to measure Flux. One hundred fold (100x) change in Flux = five (5) magnitude units.
Absolute Magnitude: The normalized brightness of stars or objects if they were all at ~32.6 light years distance (exactly 10 parsecs) from Earth. Our Sun has an Absolute Magnitude of 4.83.
Apparent Magnitude: The perceived brightness of an object in visible light from (a camera orbiting) Earth. For example: even if a dimmer star is closer - it may appear brighter.
The brighest objects have negative values (our Sun has an Apparent Magnitude of -26.5, our full moon magnitude is ~-12.7 from Earth). The dimmest objects have positive values (Polaris' apparent magnitude is about 2) and the star Vega historically anchors the magnitude scale at zero (0) for all wavelengths. The faintest object we can see with a naked eye is about magnitude 6.
Distance Modulus: The difference between Absolute and Apparent Magnitudes. The Distance Modulus for our Sun is about 31.4 (4.8 minus -26.5)
Standard Candle: An astronomical object or phenomena with a brightness that is reliable distance indicator, assumed to have constant characteristics independent of distance or age. Cepheid Variable stars and Supernova Type 1 are typically used as Standard Candles even though both have known variance.
Photon Velocity: Always the same in a vacuum - "light speed" or "c"
Cosmological Brightness Dimming: Loss of flux (brightness) due to Universe Expansion.
(This claim has no meaning outside Big Bang / Expansion models.)
Bremsstrahlung
When electrons slow down in the electric fields of other electrons or protons they emit gamma-rays called Bremsstrahlung, Gas Reradiation, Braking radiation, or "free-free" radiation.
Who bears responsibility for a scientific claim? In logic, the proponent of an idea, not a skeptic, is responsible for providing clear, unambiguous claims for the idea, all necessary definitions, the evidence and rationale. This is not always done in Cosmology.
The opposite is a logical fallacy called Shifting the Burden of Proof; a special case of Argumentum ad Ignorantiam. It is the error of putting the burden of proof on the person who questions the assertion. The fallacy's origin is assuming that something is true unless proven otherwise.On this point Big Bang lacks two fundamental definitions: which definition of space it uses, and its own definition. Notably the International Astronomical Union does not maintain a Big bang definition and probably never will. Until these definitions are completed, Big Bang is not a scientific claim. Until these definitions are complete, the burden remains on Big Bang proponents, not on a skeptic.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Burden
The tendency to only recognize evidence or reasoning that confirms an already held conclusion - even when that judgment is overwhelmingly refuted, groundless or ambiguous.
Confirmation Bias was cited by the Columbia Space Shuttle Accident Investigation Board as a leading reason why strong evidence of danger was ignored by program managers.
Many times in the history of science, prominent scientists have profoundly disregarded adequate and sometimes overwhelming, evidence contradicting and refuting the dominant paradigm of the time and dismissed perfectly valid science supporting other hypotheses.
- False Positives
Some recent "main stream" hypotheses that were defended as solid at the time, but which were subsequently refuted include N-Rays ("confirmed" by some 120 scientists in 300 published articles), and Polywater (also "confirmed" by other researchers). And less recently the complex Ptolemaic motion concepts, based on the notion that our earth was the center of our Solar system and Universe. It held up for more than 1,000 years even though it was disputed by reasonable astronomers since its origin.
An inability to understand, entertain, accept or even acknowledge alternatives after your own idea is proven wrong or shown to contradict experiments.
- False Negatives
Examples of valid science that were cast aside include -- the Plate Tectonic hypothesis which was soundly rejected for 50 years before it began to gather acceptance. Helicobacter pylori causing stomach ulcers was first observed in the 1800s. Its 1982 evidence was solidly rejected by the mainstream medical community for years, but the researchers were finally awarded a 2005 Nobel prize. There are many other Nobel Prize winners whose papers were originally rejected.
This phenomenon may have prompted the observation "Doing the same thing over and over and expecting a different result is [irrational]."
To distinguish -- Confirmation Bias is an excessively positive attitude toward one's own ideas, Congruence Bias is a wholly negative attitude to other ideas.
Cosmic Microwave / Millimeter Radiation (CMR), and
"Millimeter" may have more meaning than "microwave" by clearly identifying the peak of the radiation energy - which is near one millimeter wavelength.
(One photon at 1 millimeter wavelength has the energy of 0.001248 electronVolts.)
Cosmic Microwave Radiation (CMR) is a diffuse whole sky radiation with an energy peaking at a ~2 millimeter wavelength, which is in the microwave range.
The acronym "CMR" describes the undisputed microwave radiation independent of any contested "background" or Big Bang claims.
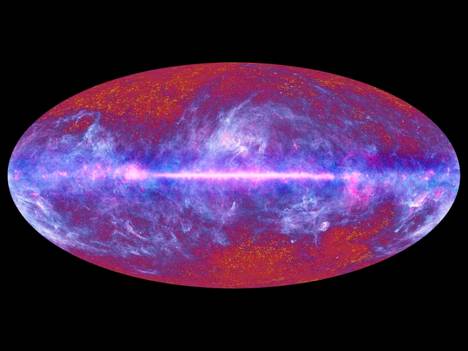 Just like most other astronomical radiation (except Quasars and Gamma Ray Bursts) Microwave (or millimeter) wavelength radiation does not show up uniformly in every sky direction. A raw whole-sky Microwave Radiation map looks extremely smooth; essentially zero variance. Processing narrows the dynamic range, adjusts the contrast and removes a dipole bias. Then a familiar dense pattern jumps out illuminating the plane and bulge of our own galaxy.
Just like most other astronomical radiation (except Quasars and Gamma Ray Bursts) Microwave (or millimeter) wavelength radiation does not show up uniformly in every sky direction. A raw whole-sky Microwave Radiation map looks extremely smooth; essentially zero variance. Processing narrows the dynamic range, adjusts the contrast and removes a dipole bias. Then a familiar dense pattern jumps out illuminating the plane and bulge of our own galaxy.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#CMR
Cosmic Microwave Foreground Radiation (CMFR tm*) is radiation with an energy peaking at a ~2 millimeter wavelength. Foreground microwave radiation includes all microwaves emitted from any kind of matter. That includes all stars, galaxies and intergalactic and intragalactic clouds of gas, dust and plasma. Foreground microwave radiation can be photographed or imaged directly; it requires no computer calculations as "background" radiation does.
Based on the Hubble Deep Field images there are millions of galaxies in every square degree of sky; all emitting Foreground microwave energy.* Just kidding. There is no trademark on the term CMFR. Though this is the first time the acronym has appeared on the web.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#CMFR
Cosmic Microwave "Background" Radiation (CMBR) is a set of interpretations of CMR claiming that the Universe expanded and cooled from a tiny hot volume (Big Bang conjecture) leaving the faint CMR radiation that is purportedly an image of the early Big Bang Universe. It is detected as microwave radiation not emitted or associated with any known foreground matter: stars, galaxies, gas or plasma. Unlike Foreground microwave radiation, microwave "Background" radiation can not be photographed or imaged directly.
CMBR advocates claim the CMR is extremely uniform (isotropic), with an energy graph/spectrum that looks like a "blackbody," and that the radiation itself has an icy temperature peak just above absolute zero at about 2.73 degrees Kelvin.
Cosmic Microwave "Background" Radiation is composed of these claims:
- The testable hypothesis that the diffuse glow of icy radiation in the microwave frequency is "background" - not from foreground sources. This claim arises from the alleged (isotropic) millimeter radiation smoothness in all directions, which, if true, would mean the CMR is not "local" (as in not from our sun, or our galaxy or even from our supercluster of galaxies). This requires the millimeter wavelength radiation is neither local (not from stars or our galaxy, or any other galaxies, nor from interstellar or intergalactic plasma, dust, gas or any other point sources) or recent (not emitted in the past 13 billion years).
- The conjecture or interpretation or opinion that Big Bang is the "background" source of this radiation, and
- The conjecture that the universe changed instantly from opaque to transparent about 13 billion years ago (Surface of Last Scattering).
- The fuzzy assertion that this "background" microwave radiation has not significantly interacted with intergalactic plasma, gas or dust in 14 billion years (Surface of Last Scattering).
Problems: While several Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work on CMR (its discovery, blackbody evidence, and anisotropy), the limitations of the evidence and rationale for "background" CMR are rarely clear or understood beyond those in the microwave astrophysics field. The CMR "background" interpretation to support the Big Bang conjecture has at least 10 severe problems with evidence, methods and rationale / interpretations.
For example the CMR "background" claim is perfectly opaque (ambiguous) on how many, if any, interactions the proposed "background" radiation photons have had with intergalactic dust, plasma, or gas in the past ~14 billion years. Leading CMR "background" advocates claim intergalactic space is vaguely "transparent" (zero? interactions with gas, plasma or dust) at least as far away as Andromeda galaxy (2.5 million light years distant). Others claim the radiation has had zero interactions with matter for ~14 Billion years .
Contrast that with the possibility of a single intergalactic photon experiencing only one interaction per year. That photon would have 2.5 million interactions coming here from Andromeda - a neighboring galaxy.
Some astrophysicists maintain that CMR is nothing more than an extremely low energy radio wave fog radiated by gas and plasma and plasma inside our galaxy called "foreground" radiation that has nothing to do with a Big Bang or expanding universe. A 2012 article explains how the angular resolution of the (COBE and WMAP) microwave "cameras" is so poor that every single "pixel" from those cameras is inextricably "infused" with microwaves from thousands of galaxies which are foreground by definition.
The excellent mapping match and high amount of Millimeter or Microwave radiation in our galaxy plane strongly indicates that a lot of its origin is from within our galaxy; that it is local and recent.
To erase or eliminate this undisputed foreground data, disparaged as "noise" or "contamination," takes a tremendous computing effort (5 months to process one year of data). The explanations for how the obvious foreground is subtracted from the maps are not clear because there is no physical difference between microwaves from foreground sources or "background." The only distinction is the location.
The discovery of this radiation is primarily credited with the decline of Steady State Models (not Static Models) and fortified Big Bang. Notably, the discovery of CMR does not interfere with Plasma or Static models. Oddly, if the Microwave Background concept ever fails it does not obviously seem to cause Big Bang's failure.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#CMBR
Concepts, Scientific Values of
Laws of Physics
Theory
Hypothesis
__________
Conjecture
Model
Laws of Physics: A scientific generalization of a physics hypothesis or theory to explain natural phenomena that has been exhaustively tested, is supported with an overwhelming set of direct evidence with no repeatable contradicting observations or a reasonable rational dispute.
Gravity, electromagnetism and the Conservation of Energy and Mass are laws of physics. Laws of physics have more scientific value than theories and hypotheses.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#PhysicsLaw
Theory, scientific: A scientific hypothesis, which has been tested in many facets and has returned replicable results with no contradictory evidence. A scientific theory has more credibility and scientific value than a hypothesis.
While ordinary conversations can use the words "hypothesis" and "theory" nonchalantly, science has strict limits on the use of those terms.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#PhysicsTheory
Hypothesis, scientific: An un-ambiguous testable idea. The bare minimum required for a scientific claim.
While ordinary conversations can use the words "hypothesis" and "theory" nonchalantly, science has strict limits on the use of those terms.
1. "Crystal Clarity" Required: No one can claim to have a scientific theory or scientific hypothesis until it is fully and un-ambiguously described; no word, term, phrase, sentence or concept may have more than one possible interpretation or understanding.
2. No claim can have "internal inconsistency;" it may not have conflicting or contradictory portions such as the fictitious ideas "Brilliant Darkness" or "Repulsive Attraction." For example: "X is bigger than a car and smaller than a bread box" are conflicting claims making it an incomplete hypothesis.
3. A hypothesis or theory must also be testable to qualify as a scientific claim.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Hypothesis
---- This line separates ideas composed with scientific rigor (above)
from other ideas (below). ----Conjecture: An idea not yet complete enough to reach the minimum criteria for a testable scientific hypothesis. It may need less ambiguous definitions, or phenomena which can be measured. A conjecture is not a scientific hypothesis or scientific theory.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Conject
Model : A tool to help understand complex phenomena by examining multiple ideas at once using adjustable conditions, assumptions and data. Models are useful for thinking through problems with many, sometimes dozens of, variables and how they affect each other. Some models are equations or formulas others are mental models. They can be physical or mathematical, static or dynamic, stochastic or deterministic, designed for optimization or simulation. Physics equations are models.
Models are best used as education tools, not as predictive tools.
Models are inherently false. Just as a map is not the landscape it depicts, mathematical or computer models never correctly mirror physical reality or natural phenomena, except perhaps for extremely simple equations (e.g. force vs distance). See Spherical Cow
A model almost never reaches the threshold of a scientific hypothesis or scientific theory because models are not required to be 1) unambiguous, or 2) to have clear definitions. Models typically include intentionally variable definitions, missing parameters and hidden assumptions. Along with their generally poor to non-existent documentation, models can too easily become "black boxes" that defy accountability.
Beware of models -- "There have been many cases in which computer models have been used to justify decisions already made and actions already taken, to provide a scapegoat when a forecast turned out wrong, or to lend specious authority to an argument." - Dr. John Sterman, A Skeptics Guide to Computer Models, 1988
Models are sometimes misleadingly called "working hypotheses" which falsely boosts their scientific value. The dramatic distinction between a model and a hypothesis is apparently not clear to far too many "Theoretical" scientists working with models.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Model
Two fundamental laws of physics stating that while mass can be converted into energy (e.g. an atomic explosion) and energy can be converted into mass, no energy-mass is created, lost or destroyed (all energy-mass is conserved) in any phenomena.
Some leading Big Bang advocates have claimed Conservation of Energy and Mass does not hold up at intergalactic distances - in spite of a complete lack of direct experimental evidence. (2)
Cosmological Constant (or "Lambda") Conjecture
(Never directly observed)
The conjectured Universe wide, uniform repulsive force claimed to be pushing our galaxies apart. (Editor's note: It might be easier to remember if it were called "Cosmological Pressure.")
But it purportedly does not act upon matter - only upon empty physical space (though it was originally intended to counteract gravity to achieve a finite static universe), and it does not affect anything smaller than a cluster of galaxies. This means it can never be tested; it inherently defies observation. It also holds the record for missing its mark by the largest error in Physics -- an almost unimaginable 120 magnitudes. (That difference makes Homeopathy's "mere" 30 magnitude problem seem trivial.)
What this means is that the conjectured energy of empty space (vacuum energy) is 120 orders of magnitude more than all the energy we observe.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#CosConstant
The assumption that on the largest scales our Universe is the same (e.g. in galaxy density and energy) from every place; that it is homogeneous and isotropic.
The assumption that our Universe is the same from every place and time.
Cosmologists
In general there are two kinds of cosmologists: Observational and Theoretical.
Observational Cosmologists use telescopes, data and physics and modest amounts of money to observe cosmological phenomena, measure it and explain it.
Cosmology Theorists primarily employ mathematics and pencils (dramatically less expensive, unless they use particle colliders like CERN's Large Hadron Collider which is the most expensive science experiment of all time.) to make up explanations for why astrophysics works.
Cosmologists are human beings who study and debate cosmology, frequently with great passion with one remarkable distinction. Cosmologists, unlike everyone else, are incapable of bias, myopia, logical or factual error or misconstructed viewpoints . . .
(While I'm just kidding there is a phenomenon which inspired the amusing bumper stickers "Cosmologists are often wrong, but never in doubt.") This may be described by the Hyper-Certainty Principle -- "Data quality and quantity is inversely related to advocacy certainty and ferocity." Thus the less and worse data available - the more certain the advocacy. This is dramatically apparent where zero data inspires huge certainty and advocacy.
The study of the largest scale structures and dynamics of our universe.
Cosmology includes the study of scientific hypotheses and scientific theories (as well as incomplete and ambiguous conjectures and models) which do not claim to have a beginning as well as those that do.
Our universe's largest structures are Supercluster complexes, Filaments and Walls of galaxies; Lyman Alpha Blobs of gas, Bubbles, and Voids with no galaxies. Some of these appear as large as 3.5 billion light years across. That's about a quarter of the distance to the farthest objects we can see and some 35,000 times larger than our Milky Way galaxy. How these structures move and change shape are some of the dynamics.
Cosmology involves the study of established phenomena including redshifts, galaxy surface brightness to distance ratios, diffuse microwave / millimeter radiation, supernova rise and decay curves, gamma ray burst spectrum stretching (dilation), galaxy rotation curves, Olbers paradox, and light element isotope abundances and ratios.
As of today these are measured only by observing photons (e.g. light, radiowaves, x-rays): the wavelengths, brightness, spectrum, emission and absorption lines and their widths, location and polarization and how these phenomena change over time, including short term pulses.
There is very little astrophysics study of extragalactic electrons, protons or anything except photons. Magnetization of astrophysical phenomena is studied indirectly by detecting the photons / light from the phenomena. (However, thousands of physicists are now studying particle collision dynamics, which does not involve looking into the sky, with the most expensive science experiment in human history (roughly twice the cost of the Hubble Space Telescope) as astrophysics.)
Cosmology also includes the study of conjectures of force and matter that have never been directly observed: Dark matter, dark energy (and its accomplices Quintessence & Phantom energy), Higgs bosons, inflation & accelerating Universe expansion, magnetic monopoles, curved space, cosmological constant (Lambda), Vacuum / Quantum Fluctuations, Virtual Particles, gravity waves, gravitons, strings, axions, tachyons, and "exotic matter."
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Cosmology
This does not mean we cannot imagine, speculate or suggest new ideas, only that if we want an idea evaluated for scientific credibility, it must provide a complete claim by meeting the minimums required for a hypothesis.
We can accurately refer to ideas which do not meet these simple criteria as "models," conjectures, concepts or stories.
The various set of Big Bang models, often called the "Standard Model," does not yet meet the minimum threshold for a scientific claim or hypothesis.
Cosmology Models
Big Bang Models
Static Models
Steady State Models
Plasma Models
Big Bang - A set of Expanding Universe conjectures or models, constructed from math equations, collectively often called "The Standard Model" where gravity dominates the largest scale Universe dynamics rather than plasma and electromagnetic effects. The models propose that all the matter and forces we now experience as our Universe originated from a hot dot smaller than an electron some 14 billion years ago and expanded (not exploded) and cooled to what we now experience.
Big Bang, widely and vigorously disputed by a growing group of astrophysicists, is not yet a complete scientific hypothesis because not even one unambiguous version exists in spite of at least 32 versions available (including Lambda-Cold Dark Matter, relativistic Friedman-LeMaitre open and closed versions, McGaugh, Einstein-deSitter relativistic, LeMaitre, Eddington-LeMaitre, Zero Kelvin models). All versions available are inherently ambiguous models, all lacking fully defined key terms including "space."
Under Big Bang some 96 percent of the Universe is either undetected, unexplained or unknown.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#BigBangModels
Static Models (Euclidean non-Expanding or ENE) - Dynamically stable (non-expanding or non-stretching Universe models, space does not "expand" with these models) galaxies and large scale structrure evolve. (Do not confuse with Steady-state models which require space expansion.)
There are two general types of Static Universe models: Open and Closed. Open or Infinite Static models were cosmology's "Standard Model" up until about 1950 and discussed for the past millenia. The newer Finite or closed version is from General Relativity prior to the Cosmological Constant invention.
Most Static models fully account for 100 percent of our Universe's matter, energy, forces and space. There is no matter that is undetected, unexplained or unknown. Static models do not require constant matter creation from "nothing" that Expansion and Steady State models need.
Almost all cosmological phenomena including Spectral-line Redshift, CMR, galaxy formation, large scale structure, light element isotope abundances and ratios, and Olber's paradox are more easily explained using Static models.
Skeptics claim Static models are weakened if galaxies from distant regions look significantly different than local galaxies. 1950's radio mapping seemed to indicate this was true. However, new Hubble images indicate the reverse; that the most distant galaxies look remarkably similar to local galaxies. Even stronger, a landmark 2013 report found that 11 Billion years ago large galaxies had the same ratio of old (red) to new (blue) galaxies. Big Bang conjectures needs far more young galaxies than old ones at that time.
Other concerns include "Tired Light" and how "remote" Type 1a Supernovas appear to fade more slowly than "nearby" Type 1as. Supernova fading seems a closer fit to expansion models than to static models. However, critics of this point respond that the error bars for the time difference between near and far supernova type 1a peak brightness is just noise - not a real signal. Another problem for Static models is that near and far galaxies appear to be roughly the same age, indicating they were created at the same time. Further, some claim that mathematics calculations make a static Universe impossible. (Of course nature is unaware of mathematics.)
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Static
Steady State (and Quasi-Steady-state) - Cosmology models claiming our Universe has relatively constant density, but is expanding (not static) and thus must have constant matter creation - from nothing.
The name Steady State can mislead because these models require an Expanding Universe just like Big Bang. Steady State models were weakened by observations indicating there are apparently more faint radio sources (and more recently quasars) at large distances than nearby. This would support the idea of a "sphere" of events occurring at the greatest distance from here. The rebuttal is that this is an Spectral-line Redshift anomaly. These models were also eclipsed and diminished by the work on "cosmic "background" microwave radiation."
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#SteadyStateModels
Plasma Models - Cosmology Models where plasma and electromagnetic forces dominate the largest scale Universe dynamics rather than gravity. Plasma models rest on the fact that most of the Universe matter is plasma and how electromagnetic forces are about 36 magnitudes stronger than gravity at the scale of a proton. There are both Static and expanding Plasma models.
Under some Plasma models all of our Universe's matter, energy, forces and space are fully accounted for.
Critics claim that even though electromagnetic forces are 36 magnitudes stronger, gravity overwhelms it at cosmological distances.
For a very rough reference in distance (not force strength): an atom's diameter is 30 magnitudes smaller than the distance to Virgo's cluster of galaxies. That larger distance is still one million times smaller than 36 magnitudes.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#PlasmaModels
Cosmology Problems
Some of Big Bang's generally accepted problems include - Flatness Coincidence, Horizon vs Light Speed Limit, Missing Magnetic Monopoles, Excess Smoothness, Arbitrary Initial Conditions, Excess Lithium, Missing Mass, Singularity violating General Relativity, Globular Clusters are too old, and the Cosmological Constant 120 orders of magnitude problem).
Other problems include Big Bang's spectral line redshift interpretation which is contradicted by abundant evidence including Binary star redshifts, Solar center-to-limb redshifts and Quasar hyperinflated Spectral-line Redshift. CMR / CMBR's's problems include its polarization, the deletion of raw Cosmic Microwave Radiation data because it is from our galaxy ("foreground"), its reheating, and the extreme improbability that the microwave/millimeter photons are "pure"; that they have not interacted with any matter: plasma, gas or dust in the billions of years of their travels.
Big Bang theorists do not discuss its more fundamental problems with science such as its failure to provide a single clear, unambiguous physics hypothesis; its failure to identify or provide a definition for "space" - independent of "space-time," or its multiple conflicts with conservation of energy and mass.
Non-Problems
The Baryon Asymmetry or "particle - antiparticle" imbalance issue is not a real problem for Big Bang because its problem claim itself is a conjecture. It is really just an interesting observation compared to Big Bang's other enormous and contradictory problems.
Static Universe Model Problems
Cosmology hypotheses without Expansion need to provide a good Tired-light hypothesis and explain Helium-4 abundance which is much higher than is explained by star processes.
Skeptics claim Static models are weakened if galaxies from distant regions look significantly different than local galaxies. 1950's radio mapping seemed to indicate this was true. Another problem is how "remote" Type 1 Supernovas appear to fade more slowly than "nearby" Type 1s. This is a closer fit to expansion models than to static models. Critics of this point respond that the time difference between near and far supernova type 1 fading is just noise - not a real signal. Also galaxies appear to be roughly the same age, indicating they were created at the same time.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#CosProblems
Critical Density
Big Bang's density threshold of space that separates the definitions of a closed Universe from an open Universe. The critical density is about 5 hydrogen atoms per cubic meter. The density of our Universe is "estimated" at about 1 hydrogen atom per five cubic meters.
This claim has no meaning outside Big Bang / Expansion models.
(No direct experimental evidence)
Similar to how light bulbs emit light, Dark Energy is emitted by "Dark bulbs" or DEDs (Dark Emitting Diodes)
(While I'm just kidding, neither Dark Energy or Dark Bulbs are scientific hypotheses.)
Dark energy is the 1990's conjecture that some unobserved energy or force permeates our Universe and accelerates its rate of expansion. Its amount is an "unimaginably low" value estimated to be about 4 electron volts per cubic millimeter - and it purportedly provides about three-quarters of all energy in the universe.
Its leading explanations are Lambda, Quintessence, or that gravity has recently (the last few billion years) acquired a new unobserved property - that it now repels as well as attracts.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#EnergyDark
Decoupling Era, or Surface of Last Scattering
The conjectured time and place when all cosmic microwave "background" radiation was produced; when the Big Bang Universe changed from opaque to transparent - some 300,000 - 400,000 years after Big Bang commenced. This is closely associated with Recombination.
This claim has no meaning outside Big Bang / Expansion models.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Decoupling
This glossary uses both "Theoretical definitions" and "Operational definitions."
Examples: Theoretical definition of Weight -- a measurement of gravitational force acting on an object (Effect of mass on Earth)
Operational definition of Weight -- a result of measurement of an object on a newton spring scale (How to weigh)
One side of physical space, as we view it from here, is "hotter" in the microwave radiation frequency than the other side. This is interpreted as meaning our solar system is moving towards the hotter side.
Distance
Astronomical Unit
Co-Moving Distance
Emission Distance
Event Horizon
Light Year
Parsec
Particle Horizon
Proper Distance
Redshift Distance
Astronomical Unit (AU) - approximately the mean distance from the Earth to our Sun; about 150 million kilometers (or 150 gigameters) or 93 million miles.
Co-Moving Distance: Distance between objects that stays the same with Universe Expansion. This contrasts with "Proper Distance" which increases with Universe Expansion. (This only applies to Expansion / Big Bang models.)
Emission Distance: The distance from here to the source of light at the time it was emitted. Astronomical objects have almost certainly moved since the light was emitted so are likely a different distance from us today. It is nearly impossible to establish a distance of movement (baseline to current position) to astronomical objects outside our galaxy since we have only been measuring distances that far for about one hundred years, a mere blink of time in cosmological terms.
Event horizon: The maximum co-moving distance we will ever be able to detect light from a particle. (This only applies to Expansion / Big Bang models.)
Light Year: 250 days. (. . . just kidding)
The distance light travels in a vacuum in a Julian year; almost 1013 (1 with 13 zeros) kilometers (or 63,000 AU). The speed of light is about 300,000 kilometers per second (186,000 miles per second).
Parsec: A distance measure used in astronomy, but less used in cosmology in favor of the "light year" which is much easier to use on large scales. A parsec is about 3.26 light years. Its short for "the parallax of one arc second."
Megaparsec = one million parsecs, or 3.26 million light years.
Particle Horizon: The maximum co-moving distance a particle could have emitted light that is reaching us today; roughly 20 billion light years. (This only applies to Expansion / Big Bang models.)
Proper Distance: Distance between objects that increases with Universe Expansion. This contrasts with "Co-Moving" Distance which stays the same with Universe Expansion. (This only applies to Expansion / Big Bang models.)
Redshift Distance: Distance to cosmological objects as measured by Spectral line Redshift. See Distance Ladder for other methods of measuring distance.
The many overlapping methods used to measure distance to astronomical objects, primarily galaxies. All these methods have significant uncertainty which increases with distance so it is probably more accurate to describe these as distance "estimate" tools.

Methods include Trigonometric Parallax, Apparent Brightness, Tully-Fisher Relation, Faber-Jackson relation, and standard candles such as Cepheid Variable stars, Supernovae light curves (questionable), and Spectral line Redshift.
Distance ≠ Velocity
While many of these other measures are used to verify Spectral line Redshift-to-Distance correlations, none can directly measure or verify the hypothesized Recession Velocity.
The "ladder" starts by measuring distances to nearby objects, then extrapolates that measure method to further similar objects, sometimes called "Standard Candles."
The Ladder's typical first rung, or starting "object" is the Pleiades cluster of seven stars. The distance to the Pleiades cluster is between 385 and 456 light years (118 to 140 parsecs). That gives the first rung of the Distance Ladder a cosmological uncertainty of about 16 percent. This means all further objects (based on Pleiades) can not have a distance uncertainty less than 16 percent.
Further rungs on the ladder use different methods (mentioned above), which are inherently less accurate.
This provides a distance estimate using the ratio of a spiral galaxy's spin rate to its intrinsic luminosity. The Faber-Jackson relation is used for elliptical (non-spiral) galaxies.
The wavelength change of sound or movement of spectral lines of light as the emitter either approaches or travels away from you.
Doppler effect is often used to simplify the explanation of cosmological redshift, and is a genuine effect seen with redshifts from the approaching side of a galaxy compared to the receding side.
However, it is not widely understood that the well established Doppler effect is not the same phenomena as that claimed for the hypothesized recession velocity, which is then used to extrapolate the Universe expansion or stretching conjecture. To explain that, a new concept called Relativistic Doppler Effect was created. This idea cannot be examined in a lab.
To support the universe-stretching conjecture, these four concepts are often entangled, or confused:
- the un-controversial well studied and established Doppler effect with
- the obscure and untestable Relativistic Doppler Effect conjecture, and
- the controversial Recession velocity (which at least is a valid hypothesis) with
- the disputed and unverifiable Universe Expansion conjecture.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Doppler
The Universe Expansion conjecture does not use Doppler Effect, it employs and requires Relativistic Doppler Effect. This conjectured form of Doppler Effect was created by Big Bang advocates to explain why redshift increases with distance (why spectral lines shift). It is distinct from standard Doppler Effect by employing Special Relativity's Time Dilation.
While standard Doppler Effect can be easily created and has been studied extensively, there is no explanation for how to physically create or study this proposed phenomena. Nor can there be until we can experiment on phenomena that does not occur on scales smaller than galaxy clusters.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#DopplerRelative
DoubleSpeak
Using words to misleadingly hide, disguise or reverse unpleasant meaning, or meaninglessness.
The Four Kinds of Doublespeak (courtesy of Prof. William Lutz)
- Hiding Meaning - Words used to avoid harsh or distasteful reality. Examples: "involuntary conversion of a vehicle" meaning your car was stolen, "Biosolids" is used instead of "sewage sludge", "anomaly" was used by NASA to dress up the deadly Space Shuttle explosion.
- Hiding Meaninglessness - gobbledygook or academia-ese. Using many impressive sounding words in a sentence that doesn't mean anything. "Gravitational waves from kinks in infinite cosmic strings." (Neither Gravitational waves or cosmic strings or their kinks have ever been observed - they are all mere
conjectures.)- Jargon (or acronyms) made pretentious or obscure. Examples: "NASA doesn't need to do an EIS under NEPA," Hemoglobin is more viscous than H20 ("Blood is thicker than water.")
- Inflated Language -- making the unimportant seem important or the simple complex. For example - "Recycling Engineer" meaning Garbage Collector, or "negative patient care outcome" meaning a dead patient.
Dynamics, Mechanics or Kinematics
Physical movement in natural phenomena caused by the ways matter and forces interact.
We try to describe changes in cosmological structure with mathematics, but because we do not know all of the dynamics or physics, mathematics can at best, only approximate how physical reality works.
The second strongest of the four fundamental forces. Thirty six (36) orders of magnitude stronger than gravity at the scale of protons. Just like gravity, electromagnetism affects things at infinite distances. Its strength decays more rapidly with distance than gravity. Gravity's strength weakens by the square of the distance, electromagnetism force (not energy) weakens by the cube of the distance.
ElectronVolt (eV)
A measure of energy and mass. Its amount is one volt times the mass of a single unbound electron. It is not an International Standard unit, its amount is determined experimentally (about 1.6 times 10 -19 Joules).
While I haven't verified the calculations for these two claims, apparently --
- One electron volt has the kinetic energy of about 40 molecules of air at room temperature.
- The kinetic energy of the protons being smashed together at CERN's Large Hadron Collider is about 14 TeraElectronVolts - roughly the energy of 14 flying mosquitoes.
The lowest speed where the kinetic energy of two objects exceeds the potential energy of the gravity and magnetic forces mutually binding them.
The minimum separation speed where two objects (i.e. a spacecraft and a planet), without propulsion, must have relative to each other which allows the two to permanently sever their re-connection, due to their mutual combined gravitational and magnetic attraction.
Escape velocity from Earth's gravitational attraction for a spacecraft at sea level at the equator is about 25,000 miles (40,320 kilometers) per hour, or about 7 miles, or 11.2 kilometers, per second; it is significantly lower at orbital altitudes.
Electrons have an escape velocity for the nucleus they orbit.
Flat (non-curved) geometry having 3 dimensions typically depicted by an X axis, Y axis and a Z axis. Some cosmology models use other geometries; the Lemaitre Big Bang Model uses Spherical Geometry which is used to solve problems on two dimensional spherical surfaces such as our planet.
(No direct experimental evidence and unverifiable)
Universe Expansion is not the same claim as the Recession Velocity hypothesis.
The conjecture that our Universe (other than galaxies) is stretching or expanding based on the observation that Spectral line Redshift movements correlate with distance; that it has expanded (not exploded) for some 14 billion years into what we experience today from a ball smaller than an electron - but not of zero size called a singularity.
This Expansion conjecture requires support from several interdependent ideas including at least three conjectures --
- the hypothesis that there is a Spectral line Redshift-to-Distance correlation - which is observed although disputed (and has a large margin of error),
- the
hypothesis that Redshift also means Recession velocity,- the
conjecture that Recession Velocity means our Universe (other than galaxies) is stretching called "Universe Expansion,"- the
conjecture that we can extrapolate the purported Universe Expansion backward in time 14 billion years to a moment when all the matter and energy in our Universe were packed together in a volume smaller than an electron.- Universe Expansion
Spectral line Redshift is explained by, not the well known and studied Doppler Effect, but a conjectured and untestable Relativistic Doppler Effect.
Universe Expansion purportedly only operates on scales larger than galaxy clusters. It does not operate at human size scales or even objects as "small" as a galaxy.
The Universe Expansion conjecture asserts that each Megaparsec (~3.3 million light years) of "space" expands / stretches at a rate of ~72 kilometers per second; or in other units -- each light-year of "space" expands / stretches at a rate of ~22 millimeters per second (or ~ 132 furlongs per fortnight - which is about 50% faster than a racing snail).
This means that for every light year an object is away from here, it should be receding from us at a rate of 22 millimeters per second. For example if a star is ten light years away from us it should be receding from us at about 220 millimeters (or 22 centimeters) per second.
"Slower" recession velocity = smaller Hubble Constant = Older Universe (under Big Bang)
Dispute: While some want you to believe Universe expansion is undisputed ("We know that our Universe is expanding") in reality the conjecture is far from settled.
Universe Expansion is not a scientific hypothesis, it is merely a conjecture for many reasons but particularly because it does not carefully or clearly define space (its primary component) or the edge of its Universe (another key component). Expansion claims our Universe has a radius ("R" is used in equations), yet at the same time it has no edge. These two claims are directly contradictory.
Recession Velocity, by contrast, is a scientific hypothesis because it clearly and fully defines its terms and it is testable and falsifiable, even though it is not yet verifiable.
Big Bang, however, depends upon this non-scientific Expansion conjecture. Failure of Expansion conjecture should mean that Big Bang fails. But because Expansion is only an ambiguous conjecture (not a scientific claim) it inherently can not fail, just like a belief, an opinion or a religion, it is not possible to conclusively refute it logically or with physical evidence.
If the Expansion conjecture is ever clearly defined and testable, it could be a scientific hypothesis - that could then be scientifically challenged.
Notably, it is not widely appreciated that Edwin Hubble, who created the Recession Velocity hypothesis was not persuaded by the Universe Expansion conjecture. Hubble did interpret Spectral-line Redshift distance correlations as galaxy recession velocity, but not as Universe Expansion (Assis et all).(3)
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Expansion
The unintentional biasing of a science experiment by the person conducting the research - generally the person collecting data. For example, a person who wants a certain outcome may find 52 coin tosses of 100 are in his favor while a video of the coin tosses shows only 51.
This effect is reduced with the use of a "Double Blind" study.
Extinction
Argument tactics that are not based on relevant facts, reason or merit.
There are hard fallacies that invalidate a claim (ambiguity, proving a negative) and soft fallacies that distract. Both make a claim false, but neither proves a claim is wrong.
Hard fallacies include Ambiguity (an incomplete claim) and Burden of Proof Reversal.
Soft examples include: Confirmation bias, GroupThink, Doublespeak, Experimenter Effect, Personality Debates, and invoking Priesthoods. For example an "ad hominem" argument ignores experimental evidence and reason and can "attack the messenger". Similarly "Appeal to Authority" also ignores experimental evidence and reason but "applauds the messenger" for their position, title, celebrity or even credibility."
Warning: The Wikipedia article has many stunningly false claims. Its theme is that there are no physical fields ! - only mathematically described fields.
Fields are physical forces produced by electromagnetism and gravity at all distances from the source. Nuclear force fields are similar except they are limited in distance. Physical fields are not quantized, they have an continuous-analog-infinity character.
Because mathematics can't easily or fully handle continuous-analog ideas (due to the infinities) mathematics artificially quantizes physical analog fields and approximates them with Scalars, Vectors and Tensors.
A Scalar is a single value assigned to each point of a field. Example: A field of grass where each blade of grass has a length.
A Vector has two values assigned to each point of a field. Example: A trampled field of grass where each blade of grass has a length and a compass direction.
A Tensor has many values assigned to each point of a field. Example: A field of grass where each blade of grass has a length, a compass direction, a width, a color, an age etc.
Filaments are sheets of galaxies forming the boundary between two or more voids. Filaments are the largest known structures in our Universe and contain almost all the galaxies, but only half the known matter. The longest filament found as of 2013 is the "Sloan Great Wall" at about 1.4 Billion light years. In January 2014, a wall appearing about six times larger is reported (~8 Billion light years across) but awaits confirmation.
(Abundant direct evidence, though less for the Weak force)
Physics has found only five fundamental forces (Electric Force and Magnetic Force are very similar in strength and character, but are not identical or equivalent):
Strong Force or Color Interaction: holds the nucleus of atoms together - only affects Quarks (not electrons), 38-39 magnitudes stronger than gravity at the scale of a proton, (38 magnitudes is astoundingly gigantic. See note below.) and is 137 times stronger than electromagnetic forces. Strong force pushes (when less than one femtometer separates neutrons and protons) as well as pulls, and oddly has a pull that increases with distance at certain ranges. Effect only reaches out to a radius of 10-14 millimeters.
Electric / Magnetic / Electrostatic / Magnetostatic: It is technically more accurate to say that there are four distinct Electromagnetic forces: Electrostatic, magnetostatic, electrodynamic and magnetodynamic. The two dynamic forces require a current flow, and two static forces with no current flow. Electromagnetic forces act on electrically and magnetically charged matter, at infinite range (as gravity does), but 35-37 magnitudes stronger than gravity. They have north and south poles (called dipole) and unlike gravity push as well as pull. A static electric charge is a monopole force. Electric field Force is measured in Volts / meter. Magnetic field Force is measured in Amps / meter.
Weak: (different from electroweak): affects Leptons (Electrons) and Hadrons (Protons and Neutrons), and is the only force significantly affecting neutrinos, 33-34 magnitudes stronger than gravity. Effect only reaches out to a radius of 10-16 millimeters.
Gravity: spectacularly weaker than the other 3 forces, acts on all known matter at infinite range and even evidently affects photons / light / radiation. It is a monopole force - unlike magnetism.
Note 1: A trillion is 12 magnitudes and a quadrillion is 15 magnitudes. A rough distance (not force) reference: an atom's diameter is 30 magnitudes smaller than the distance to Virgo's cluster of galaxies.
Force Conjectures
Wholly unobserved conjectures that new forces exist (such as Dark Energy, Cosmological Constant (or "Lambda") Conjecture). See Science Fiction.
Formation, Galaxies and Structure - (Gravity vs. Electromagnetism)
Galaxies:
The study of how matter (dust, gas, liquids, solids and plasma) organizes into galaxies.
Big Bang advocates have no reasonable explanation for how galaxies could have formed as quickly as that model requires. The only suggestion is that galaxies formed from quantum fluctuations in the aftermath of Big Bang.
Astrophysicists who prefer cosmology that is a far older than Big Bang suggest galaxies cluster from smaller particles of dust, gas and plasma, due to gravity and electromagnetic forces, since those forces exert effects at infinite distances.
Structure:
The study of how galaxies, dust, gas and plasma organizes into structures, from galaxy clusters to superclusters to filaments.
A variable number, or formula, in an equation or a model. A free parameter is appropriate for an Educational model; a model where you are trying to understand phenomena. Free parameters are rarely appropriate for a Predictive model such as a hypothesis.
In any case, employing a Free Parameter almost always prevents a model from achieving the quality and credibility of Hypothesis due to ambiguity.
According to the most cited author of Big Bang concepts, Princeton's P. James E. Peebles, the most well known Big Bang model, Lambda-Cold Dark Matter, employs and depends upon 6 or 7 Free Parameters (e.g. Baryon Density) while ESA's Planck team now identifies 19 when employing an Inflation Amendment. Particle physics "Standard model" also has 18 or 19 free parameters.
Free parameters are often misused to adjust the results of an equation or a model so it gives the pre-selected answer desired. The implication is that the number is derived from rigorous testing and meaning.
Example: If I want to claim my age is 33 years old, then in the equation for "My Age" I simply include a free parameter called "Durational Rectification" (I assign it a value of negative ten (-10) -- this year, next year it is negative eleven (-11), and so on) so I can continually adjust the result to my liking.
Albert Einstein invented a Free Parameter he called the "Cosmological Constant." He added it to his General Relativity (GR) equations so they would provide the answers that fit his changing view of the universe.
He later said this creation and use of a Free Parameter was his "greatest mistake." Many physicists believe that any use of a Free Parameter in a hypothesis is a mistake and is fundamental evidence that an idea is incomplete.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#AdjustableParameters
A notably luminous accumulation of matter and millions to billions of stars bound by gravity and electromagnetic forces.
There are two fundamental categories of galaxies based on the predominate force binding their stars as a system: gravity and electromagnetic.
1. A Gravity Galaxy is a luminous accumulation of millions to billions of stars and other matter bound primarily by gravity.
The several shapes of gravity galaxies are round: spiral, elliptical, and irregulars.
2. An Electromagnetic Galaxy is a luminous accumulation of millions to billions of stars and other matter bound primarily by electromagnetic forces. (This may be the first time this distinction has been defined.)
The several shapes of electromagnetic galaxies include: filaments, sheets, and walls.
The minimum mass and minimum number of stars to make up a galaxy is arbitrary; it appears to be around 10 million times the mass of our sun (One solar mass = M0) and one hundred million stars.
One estimate, based on the Hubble Deep Field images, claims there are at least 50 billion galaxies that we can observe.
Our own Milky Way, is primarily a Barred Spiral gravity galaxy, estimated to contain some 250 billion to a trillion stars. It is about 100,000 light years across, and 12,000 light years thick at its widest point - the center.
A spiral galaxy rotates, but at different rates at different distances from the galaxy center. This is similar to how each planet in our solar system has a different length year - the time for each planet to complete one orbit around our sun. The graph of how a galaxy rotates at different speeds related to its radius from the galaxy center is called a galaxy rotation curve.
Planet orbit velocities slow down the larger the orbit. However, unexpectedly stars' orbital velocities around a galactic center stay almost identical no matter how big the orbit gets -- once they are beyond a certain radius from the galaxy core. To help visualize this imagine all the stars of a galaxy are on the spokes of a giant bicycle wheel; all turning at the same rate together - all stars rotate around our Milky Way in one galaxy year. This surprise sparked claims of dark matter causing the orbit velocity discrepancy.
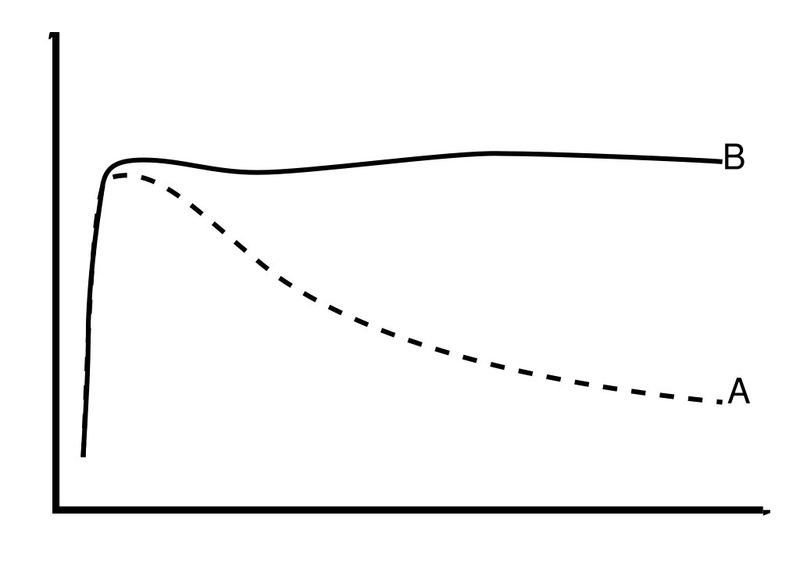
However, new calculations (Gallo and Feng, 2010) show that the observed galaxy rotation curves are completely consistent with normal astrodynamics and Newtonian mechanics; and that the original galaxy mass distribution assumptions were incorrect. This makes the purported and undetected dark matter completely unnecessary.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#GalaxyRotate
Extremely high energy, point-source short-duration bursts of radiation with very high redshifts. They typically last only a few seconds, but can last almost as long as an hour. Soon afterwards less energetic radiation (x-rays, UV and visible light) shows up from the same locations.
Satellites detect about one burst per day. They are estimated to occur about one per galaxy every million years.
Source and Distance: Unlike most other astronomical radiation, Gamma Ray Bursts show up uniformly in every sky direction - they do not show up in a dense pattern towards the center, or plane, of our own galaxy. None have low redshift values. These two things together mean that there are no close Gamma Ray Bursts. The closest recorded burst apparently occurred at about 1.6 billion light years from us, and the most distant more than 12.5 billion light years away.
One Gamma-ray burst (GRB 090423) was measured at a redshift of (z=) 8.2 making it presumably the oldest and most distant object (apparently some 13 billion light years).
There is no agreement on a good hypothesis for what causes them. Since they are so short lived it is not possible to see if they have any proper motion or to measure their distance with parallax as has been done with some Quasars.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#GRB
Spectacularly weaker than the other 3 fundamental forces, Gravity is 35-37 magnitudes weaker than electromagnetism at the atomic scale. It acts on all known matter at infinite range and even evidently affects photons / light / radiation. Its force is a monopole - unlike magnetism. Its strength decreases as the square of separation distance.
Modified Newtonian Gravity (MOND)
The idea that gravity has different effects at large scales than small scales. There is no experimental evidence for this idea.
GroupThink (or Conflict Avoidance)
A phenomena where otherwise intelligent individuals when working in a group, take a position that is contradicted by, or not supported by, all facts -- because minimizing or avoiding conflict is more important to them that making better, or even good, decisions.
This is related to Bandwagon Effect, Informational Cascades, Jante law, and Herd Instinct.
Higg's particles are hypothesized particles that purportedly provide evidence of gravity from a hypothesized "Higgs Field." They allegedly have markedly different properties from many all known particles, purportedly having zero spin. Particle physics' "standard model" says their mass should be less than 170 Gev, and researchers have looked for it at up to 800 GeV. August 2011 experiments have ruled out its mass being less than at 114 Giga-electronVolts (121 times the mass of proton) or heavier than 157 GeV.
Update: As of March 2013 a signal indicating a new particle appearing at a mass of ~ 125 GeV is now considered a Higgs boson, though not a "Standard Model" Higgs. This view is not yet endorsed by CERN in part because so far there is scant evidence the signal has any Standard Model Higgs properties.
Questions include:
1. If anything (resembling a Higgs) besides matter is responsible
for gravity, shouldn't it be everywhere? and
2. Why would such ubiquitous matter need record breaking energy
to be detected?
3. How can such a heavy particle hide so well ?
(No evidence)
A quantum field dictated by equations for the Standard Particle Model claimed to imbue many other particles with mass and gravity. It has never been detected or observed.
Homogenous means the Universe has a uniform character (e.g. density, energy, structure, shape) in general at large enough scales. Big Bang requires this to be true, however "homogenous" is an ambiguous term; there are no Standard International units to measure homogeneousness. (Editor: To provide accountability there should be a standard variance or range for density.)
"We're discovering inhomogenieties (lumps) on larger and larger scales. At the same time, the microwave background... remains smooth." "Another factor of 10 in the isotropy measurements of the microwave background could cause us to reach a real theoretical impasse." - Stanford Cosmologist Robert Wagoner, 1990
Hubble Constant, Hubble Parameter, or "H0"
The conjectured recession velocity is claimed to be directly proportional to distance as measured by Spectral-line Redshift. This ratio is known as the Hubble Constant.
This is based on the Expansion rate conjecture for Big Bang. The value is arrived at by using the redshift of an object, usually a galaxy or a supernova, to estimate its distance (non controversial) and then recession velocity hypothesis (which is disputed and unverified).
The Hubble Constant value is estimated at about ((72 km/sec) / megaparsec) +/- 8 km/sec, and as high as 90 and as low as 50.
Smaller Hubble Constant = slower recession velocity = Older Universe (and vice versa)
This claim has no meaning outside Big Bang / Expansion models.
The Expansion idea of the distance from Earth to where galaxies appear to be receding from us at exactly the speed of light; roughly where Spectral-line Redshift is about z =1.5. The current estimated value is ~ 13.75 billion light years (plus or minus 10%).
Galaxies closer than the Hubble distance or length are not receding as fast as the speed of light; further galaxies are receding faster. It is calculated with (Hubble time) times the speed of light.
This claim has no meaning outside Big Bang / Expansion models.
The linear relationship between redshift and distance coupled with recession velocity. (Recession velocity = Hubble Constant times Distance)
This claim has no meaning outside Big Bang / Expansion models.
Hubble Time
The age of the Universe according to Big Bang; roughly 13.7 billion years (plus or minus 10%). Hubble Time and the Hubble Constant ("H0") are reciprocals.
InterGalactic Medium or IGM (vs. Intra-galactic or InterStellar)
Intergalactic means the spaces between galaxies. This region contains about half of all normal matter at a very low density in the form of gas, dust, plasma, cosmic rays, and electromagnetic photons of all wavelengths and magnetic fields from gamma rays to radio waves.
Intra-galactic means within, or inside of, a galaxy.
The idea that our Universe is generally the same in all directions in the sky; that there is no special density or phenomena in any particular direction.
An-isotropy means non-uniformity - the opposite. If the Universe were Isotropic, it would not be possible to make a map of the largest structures including Voids, Walls, Filaments - because structures could not exist; everything would be wholly uniform in every direction and there would be no phenomena such as the "Great Attractor."
Extremely powerful focused flows of plasma ejected from galactic centers or Blazars at near light speeds, sometimes reaching hundreds of thousands of light years in length. Some jets appear to exceed the speed of light.
Jean's Instability
The simple idea that areas with large amounts of matter will attract and collect other matter due to gravity.
Most gasses cool when expanding. Surprisingly, Hydrogen, Helium and Neon warm when expanding at room temperature due to a conversion of molecular kinetic energy to potential energy. Total energy remains the same, but the conversion results in an increase in molecule collisions causing warming. Hydrogen, Helium and Neon do not obey the "Ideal Gas Law" because that idea ignores molecular size and intermolecular attraction.
"Lambda Cold Dark Matter" is probably the most well-known and most popular of the several dozen Big Bang / Expansion models. It "assumes conventional local physics, general relativity theory, expansion from a hot big bang with initially small adiabatic gaussian near scale-invariant departures from homogeneity and isotropy, cold dark matter, Einstein's cosmological constant, and negligible space curvature." (courtesy of Princeton's P. James E. Peebles)
This model produces the remarkable claim that ~ 95% of our Universe's matter and energy is undetected, unobserved or unknown to physics. Neither the conjectured dark matter (~ 23%) or Dark Energy (~ 72%) has ever been directly observed. Lambda stands for the Cosmological Constant.
(No experimental evidence)
The hypothesis that magnetic solids having a single pole exist. Normal magnets have two poles, a North and a South Pole, called a dipole object. A monopole would only have a North pole or a South Pole - but not both.
None have ever been detected (though an Electron looks suspiciously like one, except it is deemed an "electric monopole."
Magnetic force with no electric current flow; distinct from electro-magnetism and electrostatics.
Permanent magnets exhibit magnetism with no electric current flow.
Stars with the most powerful magnetic fields known. Suspected to be extremely dense Neutron stars.
Magnitude
Two meanings:
- The brightness of astronomical objects on a logarithmic scale, or
- A measurement difference of ten times - eg. 100 is one magnitude (one zero) larger than 10. and One million (1,000,000) is five magnitudes (five zeros) larger than 10.
The inability to see fainter galaxies (or other phenomena) and only see the brighter galaxies as we view things at the limits of our telescopes (e.g. at the edge of our visible universe).
This causes the mean (average) luminosity of objects and phenomena to appear to increase with distance - which is not correct. This phenomenon occurs with all astrophysics phenomenon.
Its similar to trying to establish the mean (average) age of residents of a distant island using a telescope, but omitting the ages of the children because they are too small to see.
A language or shorthand used to help understand quantities, abstractions, and scientific and logical relationships. Math can be used as models of natural phenomena. However use caution because "Models are inherently wrong."
Beyond basic trigonometry, algebra, coordinate geometry, calculus and orbital mechanics, Cosmology Theorists often use Lorenz Transforms, Riemannian Geometry, Tensor Calculus, Eigen values and vectors, Hamiltonian mechanics, Lagrangian Density, and General Relativity.
While these tools may sound daunting at first, taking each one slowly and with a bit of practice they are not hard to understand and they can be useful. (OK, I admit maybe General Relativity is seriously opaque.)
However, do not confuse mathematics with physical reality; physical reality does not care one bit about mathematics. Similar to how a wild shark doesn't care if you call him Sherman or Megan, mathematics is just a set of labels we use to help us understand how physical reality works.
Mathematical correctness, integrity, existence or precision is not proof that there is any corresponding physical reality. For example the square root of negative 7 acres has no physical reality; for that matter negative 7 acres (-7) has no physical reality either.
* Universe Dynamics Understandable without Math
Fully appreciating how some friends and colleagues might consider this blasphemy ;-) it is this author's opinion -- that in the same way that you can successfully drive a car without needing to understand the math of vehicle dynamics, it is similarly not necessary to understand the many fields of higher mathematics to understand the dynamics or physics of cosmology.
While it can be helpful for some to understand the math, it is not required. Math is only another tool, in this case a language or shorthand, to help you understand the dynamics of natural physical phenomena. (Mathematicians should recall how Mathematics has its own overarching intractable problems including Godel's Incompleteness Theorems.)
"A mathematician is a device for turning coffee into theorems" - Paul Erdos
Matter (confirmed)
Anti-matter
Baryons
Dark Matter
Electrons
Hadrons
Leptons
Neutrons
Protons
Quarks
Anti-matter is the same as ordinary matter (electrons, neutrons and protons, and all fundamental particles: quarks and leptons having a rest-mass and volume) in every way with one electric exception.
The only difference is anti-matter is composed of otherwise identical particles with a reversed electromagnetic charge. Those particles (e.g. anti-quarks, anti-protons) are called anti-particles.
There is nothing fundamentally different about anti-matter (it exhibits and is affected by gravity, not anti-gravity, just the same as ordinary matter). Just like plasma, it is just very rare on Earth's surface. We are familiar with ordinary matter, which is dramatically more common here on Earth. You may experience the rare anti-matter here on Earth when taking a medical PET scan where Positrons are used. Anti-matter is more common above our atmosphere in the Van Allen belts where it occurs naturally.
Anti-matter does not have negative mass, only particles with positive mass and (like a collect call) reversed charges.
While it is true that combining a particle and its anti-particle will explode, there is absolutely no evidence that an explosion results when mixing pasta and antipasto ;-)
Baryons - Protons and Neutrons and other subatomic particles made up of 3 quarks governed by the Strong nuclear force.
Bosons - are Photons, gluons and other Force-carrying "particles." The W, Z and Higgs Bosons are extremely short lived, less than a microsecond.
Dark Matter: Matter which does not emit detectable radiation.
There are two kinds of dark matter:
1. Real physical matter - Non luminous ordinary matter including solids, liquids, gas, and plasma, such as dust which interacts with gravity, light and other radiation.
2. A conjectured, never observed, highly speculative "missing" matter that does not interact with light, other electromagnetic radiation, other particles or even itself except for its apparent gravitational effect on galaxy rotation - making it undetectable directly. Big Bang needs gigantic amounts of this kind of dark matter. It is commonly conjectured to compose 22 percent of the Universe, with known mass composing only 4 percent. This means Galaxies must have 5.5 times more Dark Matter than ordinary real, physical matter.
This missing Dark Matter idea arose from calculations that appeared to show that galaxy rotation curves were not explainable using Newtonian and Keplerian physics. The original calculations used the Virial Theorem to estimate that a galaxy had 160 times more matter than was visually observed. Some also advanced the claim that without the gravity of huge amounts of conjectured dark matter a galaxy would fly apart.
However, a new approach and calculations (Gallo and Feng, 2009) show that the original galaxy mass distribution assumptions were incorrect and that galaxy rotation curves are completely consistent with normal astrodynamics. This means galaxy rotation curves are fully compatible with the normal observed matter; that no dark matter is necessary.
Electron (a Lepton) - A negatively charged particle usually found orbiting an atomic nucleus. Until recently considered fundamental; not composed of smaller particles. Now it seems that an electron has been separated into three parts: a Holon, a Spinon and an Orbitron.
Fermions - Fundamental particles including Electrons, Quarks, Neutrinos, Taus, Muons and their anti-particles.
Hadrons - all particles made up of Quarks and held together by the Strong force: Protons, Neutrons (Baryons) and Mesons.
Leptons - Electrons, Neutrinos, Positrons, Muons, Tauons which are not subject to the strong force, but are affected by gravity and electromagnetic forces.
Matter, Ordinary - Substance with rest-mass, volume and energy.
Mesons - Unstable subatomic particles made up of 1 quark and 1 anti-quark. Interesting, but nearly useless.
Metals - In Cosmology, all elements heavier than Hydrogen and Helium are called metals.
Neutrons - a subatomic particle with no net electric charge made up of 1 up quark and two down quarks.
Neutrino - a subatomic particle with a large amount of energy, extremely little mass, but no net electric or strong force charge. They are only affected by the Weak Force and Gravity making them exceedingly difficult to detect.
Protons - Tons which have discarded their amateur status. (Pro - Tons... just testing to see if you are paying attention :-)
A subatomic particle with a net positive charge composed of two up quarks and one down quark. (Except they don't even come close to adding up correctly. A proton "weighs" some 938 MeVolts, while three quarks together don't exceed 16 MeV.)
Quarks - are considered the most fundamental particles. Protons, neutrons and electrons are composed of Quarks. Individual Quarks have never been observed.
Tachyons - Imaginary particles that only travel faster than the speed of light.
Tetraquarks - Hypothetical Meson composed of 4 valence quarks. Possibly found in 3 different type experiments.
WIMPS - Weakly Interacting Massive Particles. Never observed hypothetical particles intended to solve the missing dark matter problem, that are massive, yet not affected by Electromagnetic or Strong forces. Like Neutrinos, they are only affected by the Weak Force and Gravity.
Absolute Motion
Apparent Motion
Proper Motion
Peculiar Motion
Peculiar Velocity
Parallax
Absolute Motion vs Apparent Motion
Since our Universe has no inherent center or starting point (no X,Y,Z coordinates equalling 0,0,0), Absolute Motion is movement with respect to our Sun, or Milky Way's Galactic center, or our Local Cluster.
Since all reference points are moving relative to others, to determine distances and relative motions for each measure we must choose a specific location as a starting point; an inertial rest frame.
The most common in Cosmology are --
1. Absolute Motion (S*) for motion relative to our Sun,
2. or a closely related location called Local Standard of Rest (LSR),
3. Absolute Motion (G) for motion relative to our Milky Way's Galactic center,
4. Absolute Motion (C) for motion relative to our Local Cluster's center.
Apparent Motion: All stars and galaxies have 3 dimensional motion relative to Earth. With close objects we can sometimes discern transverse star movement (meaning sideways or up and down) with great accuracy. However, as distances increase we cannot determine transverse galaxy motion with much accuracy or confidence. This uncertainty is why it is called Apparent Motion. The difference between Absolute Motion and Apparent Motion can be small or dramatic.
One extreme example is a geostationary satellite.
Absolute Motion (Relative to any point on Earth) = zero; Apparent Motion = zero.
Another example is a Meteorite zooming straight towards you. It has zero sideways motion, but very high approach motion. (This actually happened to me once, and Yes, it curved off before it got to me.)
Absolute Motion (Relative to me) = high; Apparent Motion = Zero.
Another extreme example is the moon. Relative to our Earth,
our Moon has a small (but measurable) motion towards or away from us,
yet it has an obvious high sideways or transverse motion.
Absolute Motion (Relative to Earth) = high;
Apparent Motion = high and identical.
(*Note 1: The notations S,G, and C are my suggestions.)
(Note 2: Since there is no Universal Reference Frame, it is not always clear which of the several Absolute Motion reference frames are used for determining/claiming light's absolute speed.)
Peculiar Motion: Motion of a star compared to its neighbors.
Peculiar Velocity: Motion of a galaxy compared to its neighbors. In the context of Big Bang's Expansion conjecture, Peculiar Velocity is any movement of a galaxy towards or away from our sun that is not attributed to Universe expansion or stretching. It is most often used to distinguish an individual galaxy's velocity that is different from its "host" galaxy cluster.
Proper Motion: Peculiar Motion + motion relative to our Sun.
Proper Velocity: Peculiar Velocity + motion relative to our Galaxy that is independent of Spectral-line Redshift.
Parallax: Apparent change in location of a star due to two observation sites. A star could have a parallax, yet no motion relative to our Sun.
A cloud of intergalactic or interstellar gas. The Hubble space telescope has captured some spectacular (though typically color "adjusted") images of some nebulae.
Big Bang Nucleosynthesis / Light Element Isotope Abundances ("BBN")
A set of Big Bang dependent conjectures claiming that almost all of the lightest four element isotopes existing today were created in the first few moments of Big Bang including ( Hydrogen (Deuterium or H-2) and Tritium (H-3), Helium (He-3 and He-4), Lithium (Li-6 and Li-7) and Beryllium (Be-7 and Be-8) ).
This claim is disputed with the hypothesis and mounting evidence that all light element isotopes can be created / converted by normal star processes (stellar nucleosynthesis), and that the BBN idea depends upon the arbitrary and extraordinarily precise initial conditions of a baryon to photon ratio of 6 to 1.
Occam's (Ockham's) Razor (Law of Parsimony)
The philosophical guideline (not a scientific law, theory or hypothesis) that if every thing else is roughly equal, the simpler explanation is preferred.
The claim of a conflict between the apparent darkness of the night sky and the concept of a static, infinite universe. It is claimed to diminish static universe models because an infinite static Universe should radiate light from every sky direction making night bright.
However, we now know that about half the known matter (dust, gas and plasma) is spread outside of galaxies. This makes Olber's proposal that most distant star and galaxy light is absorbed by that matter and re-radiated as non visible (e.g. infrared) radiation - reasonable.
Omega (space curvature criterion)
The mass density parameter, relative to the Hubble Constant. The mean matter density divided by the "critical value" of that density.
For those who believe space has an overall curvature (separate from general relativity's space-time curvature), if Omega equals 1 it means space is flat, if greater than 1 "the Universe is closed" (like a sphere), and if less than 1 the Universe is "open" (negatively curved like a saddle !?).
This claim has no meaning outside Big Bang / Expansion models.
Personality Debate
A non-scientific argument about who asserts something rather than what is claimed, common with "priesthoods." A stunning and dismaying amount of Big Bang "debate," by those who should know better, is "who" based rather than "what" based. Similar to a Technology debate - which ignores principles to focus on the technology. See Logical Fallacies and Hyper-Certainty Principle.
Photons (Light and the rest of the electromagnetic spectrum -- from most powerful to least)
Gamma rays
X-rays
UltraViolet (UV)
Visible Light
InfraRed waves
Microwaves
Radio waves
Photon: The smallest unit of electromagnetic energy. They have no electric charge or rest-mass. The following are in order of decreasing energy per photon.
Gamma rays: The most powerful radiation / photons: more energy than visible light, UV or x-rays. Damages DNA and can kill living cells. Most Gamma-rays are absorbed by oxygen in our atmosphere. Emitted from atomic nuclei transitions.
X-rays: More energy than light or UV. Known to damage DNA. Most X-rays are absorbed by oxygen in our atmosphere. Typically emitted by electron transitions.
UltraViolet (UV): More energy than light. Known to damage DNA. Most UV is absorbed by ozone in our atmosphere, the remaining UV that gets through can cause skin cancer.
Visible Light: What our eyes see. Most visible light gets through our atmosphere. Should not damage DNA.
InfraRed waves: Heat that we can feel with our skin. Should not damage DNA (unless your body gets hot enough to catch fire).
Microwaves: Heat also, but each photon has less energy than an InfraRed wave. Most microwaves are absorbed by our atmosphere, though some microwaves get through. (Wavelengths are 1 millimeter to 1 meter)
Radio waves: The least energetic photons, less energy than light or heat. Most radio waves get through our atmosphere. (Wavelengths are longer than one (1) meter)
Photon Echoes
The (very clever) study of timing of light from a variable star and the reflections of that light on a close cloud of relatively dense gas or dust either directly or after diffusion by the cloud. Using the variability of the star, the lengths of both paths may be compared, so that a 3D image of the system may be drawn. This was demonstrated with the Supernova SNR1987A. (explanation courtesy of Jacques Moret-Bailly)
Plasma is a fourth phase of matter that is different from gas, solid, and liquid. It is similar to a gas but is highly electrically conductive because it is partially ionized. This makes it strongly responsive to magnetic fields at astronomical distances.
Although plasma is overwhelmingly the most common form of matter in our Universe few scientists and almost none of the general public are familiar with it.(Ionized liquids and solids also exist, some with extraordinary properties, but they are exceedingly rare.)
All luminous stars are made of plasma, and even the space between stars and galaxies is filled with plasma. About the only places in the Universe lacking plasma are the great Voids and the thin surface layer of planets with an atmosphere - exactly where we live.
Cold: Plasmas can exist at almost any temperature. Plasmas can be searingly hot (millions of degrees), at room temperature or surprisingly as cold as superconducting temperatures (a few degrees above zero Kelvin).
Thin: Plasmas can also be very rarefied. A gas with only 1% of its particles ionized can exhibit high electrical conductivity and other plasma characteristics. These two phenomena together (cold and thin) are conditions common in outer space.
Shapes: Plasmas regularly form non-circular shapes including filaments and sheets.
Some scientists mistakenly believe that the space between galaxies is charge neutral, thus nullifying any large scale structure effect by magnetism. Because plasma inherently has an electromagnetic charge, this means the space between galaxies is charged, is affected by magnetic forces and not merely by gravity.Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Plasma
Misleadingly called "Acoustic" Oscillations, this idea has nothing to do with acoustics and is only extremely remotely related to gas pressures.
This conjecture claims that regions of plasma pulse in density, due to gravity and gas pressure, but puzzlingly not due in any part to electromagnetic forces which are 36 magnitudes stronger. (See Baryon Acoustic Oscillations)
The deliberate effort to make a subject (e.g. surfing, economics or cosmology) intimidating or complex as opposed to easy, approachable or understandable, implying the "insider" is superior to ordinary mortals. An easy way to recognize a Priesthood is the abundant use of unnecessary jargon or code words (including mathematics) for phenomena easily and more clearly explained with common words.
For example this glossary uses the marvelously obscure (but fun) "Furlongs per Fortnight" to spoof the silliness of the rate of the conjectured "Cosmological Constant" which is given in a similarly obscure and confusing (but gravely serious and possibly doublespeak) unit of measure -- "kilometers per second per megaparsec."
Quasars are point-sources of continuous radiation with apparently extremely high redshifts, unusual spectra with a non-thermal spectrum, broad spectral lines and almost no absorption lines. Appearing frequently as blue in color, some 200,000 have been found, most by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Although they emit continuous radiation, their brightness can vary dramatically over a period of weeks.
Because of their apparent extreme Spectral-line Redshift, Quasars appear to be the most energetic, point-sources of continuous radiation known. A single quasar can appear to emit as much energy as a thousand galaxies.
Quasar Quandry (Distance Conflict): Quasars have dramatically conflicting evidence for their distance from us:
1. Quasars appear to have extremely high Spectral-line Redshifts. None have exhibited low Spectral-line Redshift values (the lowest as of 1995 is z=0.173 for PKS-2349-014). If correct, the closest quasar (PKS-2349-014) would be more than 1.5 billion light years away from us. This would put the closest Quasar 15 times farther away than the diameter of our local Virgo supercluster of galaxies. That would mean there are zero Quasars in any of the thousands of our neighboring galaxies.2. And unlike most other astronomical radiation, Quasars, like Gamma Ray Bursts, show up uniformly in every sky direction - they do not show up in a dense pattern towards the plane or center of our own galaxy.
Extremely Far? -- These two things together suggest there are no close Quasars; that the nearest Quasar is no closer than 1.6 billion light years from us - some 16,000 times our galaxy's diameter. The most distant quasar appears to be 28 billion light years away. Because they appear to exist only at great distances, they are conjectured to have only occurred long ago, at times closer to the conjectured Big Bang.
3. However, a handful of quasars (e.g. PHL 1033, TON 202, LB 8956 and LB 8991) seem to show proper motion (meaning they appear to be moving across the sky) which almost irrefutably indicates they are nearby; they must be within our own galaxy - even though they exhibit high redshifts.
4. Quasars sometimes eject matter at velocities that appear to exceed 10 times the speed of light (superluminal) if they are extremely distant. However, if Quasars are nearby, within our galaxy, then the jet/ejecta would obey the light speed limit.
5. Quasars almost complete lack of absorption lines also supports the idea of close Quasars because light must travel through large gas or plasma clouds (much larger than our galaxy) to accumulate absorption lines. There is not yet any reasonable explanation for how radiation from 200,000 sources at cosmological distances rarely passes through gas clouds. (Quasars do exhibit metal emission lines)
6. There is growing evidence many quasars are physically associated with low-Spectral-line Redshift (close!) galaxies.
Extremely Close? -- These last four lines of evidence raise the serious likelihood that Quasars are (relatively) nearby. This means the high Quasar Spectral-line Redshift numbers could be indicating distances magnitudes beyond the Quasar's actual distance from us. This would also mean that Spectral-line Redshift has a dramatically larger variance or margin of error than generally thought, and its correlation as a distance indicator is seriously unreliable.
Conflict Needs Resolution -- Because quasars have such high Spectral-line Redshift indicating colossal distances and proper motion indicating nearness, we must reject either the proper motion experimental evidence or the Spectral-line Redshift interpretation. Since proper motion is directly observable evidence and Redshift-distance correlation is only an explanation or an interpretation, the explanation has far less strength than the direct experimental evidence of observable sideways motion. The evidence that quasars are nearby seems stronger, and unfortunately as a side effect Redshift loses. This seems a serious problem for Big Bang, and a potential problem for GPS systems using quasars for reference.
Energetic: According to redshift interpretations, if there are apparently no close Quasars, they are highly energetic, apparently the most luminous phenomena in the universe. If they turn out to be closer than Redshift-distance correlation tells us - they are less luminous.
If they are as distant as Redshift-distance correlation tells us -- they are hypothesized as compact regions surrounding the center of massive galaxies, very similar to Active Galaxy Nuclei.
Note: While Gamma Ray Bursts typically last only a few seconds, Quasars radiate continuously, while fluctuating over a period of days to months, making them candidates for measuring distances as standard candles - after their serious redshift problem is solved.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Quasars
Recession Velocity (or radial velocity)
(Recession Velocity is not the same claim as Universe Expansion.)
Recession Velocity is a three-part hypothesis, an interpretation of Spectral line Redshift claiming that --
- distant galaxies are receding away from us,
- at a velocity proportional to redshift values,
- assuming redshift values only mean velocity.
Recession Velocity is not the same as Universe Expansion. Universe Expansion conjecture is a separate claim, a complete change of physics and one giant leap of imagination away from mere Recession Velocity in that some Galaxies can certainly recede from us without invoking Space expansion.
Recession Velocity's value is estimated at about (( 72 km/sec) / megaparsec) (+/- 10 percent) (or 22 millimeters per second per light year) and as high as 90 km/sec/mp and as low as 50 km/sec/mp.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Recession
ReCombination
The conjecture that CMR "background" was released about 300,000 - 400,000 years after Big Bang. This is explained as when Big Bang energy had cooled to about 3,000 deg. Kelvin and condensed protons and electrons into neutral Hydrogen and Helium atoms. This is closely associated with Surface of Last Scattering.
Prior to ReCombination charged particles were so close together photons could not escape -- making the Universe opaque. However, immediately after ReCombination - photons had absolutely free rein - nothing to run into (no matter).
(The term "ReCombination" was borrowed from physics. Since there was no prior "combination" don't let the prefix "Re" mislead you.)
This claim has no meaning outside Big Bang / Expansion models.
Redshift occurs when spectral lines of light or other electromagnetic radiation from astrophysical objects (like galaxies) shows up in longer wavelengths than normal (compared to those in a laboratory experiment), apparently resulting in energy loss. It is the primary measuring "stick" used to estimate cosmological distances. Spectral-line Redshift is measured several ways, in several wavelength bands (but surprisingly rarely in the visible light range), has a huge variance that is not widely grasped, and is apparently caused by several independent phenomena.
Blueshift is the reverse - when spectral lines move towards shorter wavelengths apparently meaning an increase in radiation energy. Blueshift has been observed in radiation emitted by stars and galaxies moving towards us. There are quite a few (at least 600, possibly almost 7,000) generally nearby galaxies exhibiting Blueshift.
Importance: The interpretation of Spectral line Redshift as Universe expansion is the primary support for Big Bang models.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Redshift
Several sets of co-orbiting stars called Binary stars, each of which inherently maintain equal mean distances from us, show consistently different redshifts (e.g. Binary HD193567 and several Wolf-Rayet Binaries).
The graph depicts the redshift from two co-orbiting stars and how it changes for each during their orbits. Notice how each star has very different maximum and minimum redshift.

This Spectral-line Redshift is clearly a different redshift phenomena from the Universe stretching or expanding conjecture. Incidentally, many stars come in binary pairs or triplets; of our closest 30 star neighbors only 7 lack co-orbiting companions.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#RedshiftBinary
Redshift, Dipole or "Spectral Transfer"
An experimentally demonstrated mechanism which is linear in intensity and maintains the direction of the propagation of the radiation. It involves the Dipole force interacting with atoms and the Ponderomotive force interacting with electrons. The two combined are called "Spectral Transfer Redshift." (L. Marmet 2009).
Dipole force is wavelength dependent and can be distinguished from Doppler effect. Ponderomotive force is independent of wavelength and mimics a Dopper effect.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#RedshiftDipole
The hypothesis with experimental evidence that light loses energy by increasing in wavelength when leaving a strong gravitational field. Oddly, there is apparently no evidence of gravitational Spectral-line Redshift from our own sun.
Our Sun's equator and poles (limbs) show consistently different spectral line redshifts even though they are not moving away from us over the course of a year (they inherently maintain equal mean velocities away from us - essentially zero kph or mph). This Spectral-line Redshift is not a reddening due to atmospheric absorption, or "Limb Darkening" (a decrease in optical brightness from Center to Limb). Some astrophysicists claim this could be explained by Bremsstrahlung or the Compton effect
This Spectral-line Redshift is clearly a different redshift phenomena from the Universe stretching or expanding conjecture.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#RedshiftSun
Redshift, K-effect
In our own Milky way galaxy --
- Bright blue stars are Spectral-line Redshifted by about 10 km per second compared to neighbor stars.
- O-stars are redshifted by about 10 km per second compared to B-stars, and
In neighboring galaxies, Red giants are Spectral-line Redshifted by about 10 km per second compared to other stars.
These three phenomena are collectively called K-effect redshift.
This phenomena which undermines the standard redshift explanation is unexplained.
Redshift, Companion or Child Galaxy
All of Andromeda's smaller child galaxies have higher redshifts than the "parent" galaxy. All eleven of Andromeda's companion galaxies have higher Spectral-line Redshifts than the "parent" galaxy. Statistically, half of all these "child" galaxies should have lower redshifts or even blueshifts if they are orbiting the parent, yet none do.
This phenomena which contradicts the standard redshift explanation is unexplained.
When high energy radiation hits an atom, photons are ejected at a reduced energy and at an angle.
Redshift, Electron Recoil
The hypothesis that whenever an electron emits a photon - it recoils by a tiny amount - making the resulting photon slightly less energetic than the one that originally hit the electron. As the number of electron interactions adds up the photons eventually lose enough energy that the loss can be detected - making "Tired Light."
The conjectured event (at about 100-400 million years after Big Bang) that purportedly dramatically re-heated CMBR so it would not remain colder than its current temperature of about 2.73 deg. Kelvin.
If the conjectured CMBR was allowed to cool uniformly (after being created by ReCombination), it would be too cold (less than 0.1 deg K) compared to current CMR observations. Thus it could not support the CMBR-Big Bang conjecture. So the ReIonization conjecture was designed to warm up Big Bang's conjectured CMR to match the observations.
There is no compelling explanation for what physics could have caused this reheating (stars? quasars?).
This claim has no meaning outside Big Bang / Expansion models.
Relativity, Special (or as Einstein preferred "Invariantentheorie" or Invariance Theory)
The generalization of Galileo's relativity principle that there is no absolute condition of rest, and that all uniform motion is relative. It does not incorporate gravity, or relative speeds approaching the speed of light and only applies to local (ambiguous) objects moving relative to each other.
It includes the idea that the speed of light is the same for all observers - no matter how they are moving. It asserts that no particle with mass can reach the speed of light relative to another particle. The equation E=mc2 (Energy = Mass times the speed of light squared) preceded and is derived from, but is not dependent upon, Special Relativity.
Special Relativity was intended to solve the problem raised by the 1880s Michelson-Morley experiments that found light going almost exactly the same speed independent of the direction light speed was measured. This is taken as lack of evidence for aether. (Remarkably, even the most recent versions of these experiments have not found zero difference in the speed of light going with Earth's rotation and against it, though the uncertainty bars do include zero.)
Critics point out that laws of physics must apply universally not just locally; and that two particles approaching each other each at speeds of 99 percent of the speed of light (a standard experiment at particle colliders, and adding up to almost twice the speed of light) violate Special Relativity's speed limit.
The mathematics of special relativity is logically consistent (locally) but there has been "a failure to understand special relativity as a theory of physics." (Lawrence Stephenson, 2000-2010)Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#RelativitySpecial
Big Bang / Expansion models are dependent upon and directly derived from General Relativity's Field equations.
Non-Linear (meaning curves and multiple dimensions) Differential Geometry Equations which add gravity to Special Relativity so it can apply to any two objects - no matter how far apart. General Relativity needs Solutions to anchor its predictions to anything resembling physical reality.
It is also considered a framework for understanding the behavior of space-time. Its equations predict an unlimited, and a potentially infinite, number of phenomena including gravitational lensing, gravitational Spectral-line Redshift, gravitational waves and Mercury's perihelion precession.
General Relativity uses field (analog) concepts, as opposed to Quantum physics which assumes everything in physics is digital. General Relativity claims that space is curved. It also claims space and time are not independent; that they directly affect each other.
Notably - General Relativity does not require conservation of energy and mass.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#RelativityGen
Science is a way of understanding fascinating natural phenomena so that it can be generalized, predicted and relied upon at other times and places. It has two parts: A way of testing hypotheses (scientific method), and the body of facts that result from those tests.
No scientific fact is ever 100% certain: Facts established by careful fully-documented experiments (aka scientific method) are inherently tentative, though the more confirming experiments - the stronger the fact. The strongest facts established by scientific method are probably gravity and electromagnetic forces - even though we still don't understand them completely.
Weakest link kills or limits scientific value: No idea can have more scientific value than the weakest link in its rationale. For example -- if an idea depends on four sub-ideas where three of them are valid hypotheses or even theories, but one is an incomplete conjecture (e.g. Astrology) - the idea is not a scientific claim. The conjecture is the weakest link making the valid hypotheses irrelevant. The only way to salvage such an idea is to limit the hypothesis to the two or three remaining complete scientific claims.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Science
Imagined phenomena or technology without physical experimental evidence, some contradicting a fundamental law of physics, used in novels imbued with technology and space travel. Sometimes found sneaking into mainstream science publications.
"Alice laughed: "There's no use trying," she said; "one can't believe impossible things."
"I daresay you haven't had much practice,"said the Queen. "When I was younger, I always did it for half an hour a day. Why, sometimes I've believed as many as six impossible things before breakfast." - Alice in Wonderland.
Dismissed cosmology ideas:
Aether (well-entrenched physical law until the early 1900s), phlogiston, Ptolemaic motion (complex earth centered Universe idea that lasted 1,000 years).
Current cosmology ideas contradicting fundamental Physics:
Negative Energy, Anti-(or negative)-Mass, multiverses.
"Invisible" or mythological cosmological phenomena as of Jan 2014 (absolutely un-observed, no direct experimental evidence):
Dark matter, dark energy (and its accomplices Quintessence & Phantom energy), cosmological constant (Lambda), inflation, accelerating Universe expansion, magnetic monopoles, curved space, gravity waves, gravitons, strings, axions, "exotic matter," scalar fields, tachyons, worm holes.
Disputed cosmology and Big Bang interpretations as of Jan 2014:
Essentially every important topic including Spectral-line Redshift-to-Distance correlation, Spectral line Redshift meaning Universe expansion / stretching, Tired Light, CMR as background, galaxy rotation needing dark matter, accelerating Universe expansion, nucleosynthesis, Olber's Paradox, supernova rise and fall curves.
Undisputed cosmology phenomena as of Jan 2014 (with strong evidence or reason):
None. Essentially every phenomena in cosmology (not astrophysics) is disputed. Perhaps the only phenomena that is generally agreed to is that Spectral line Redshift can sometimes (not always, e.g. Quasars) be used as a rough distance, not velocity, indicator.
The reflex-like rejection of new knowledge because it contradicts entrenched norms, beliefs or paradigms.
Named for a Viennese doctor who methodically discovered in 1847 that when doctors washed hands with a disinfectant - deaths from a childbirth disease reduced by tenfold, to near zero, yet many of his colleagues fought this new idea delaying widespread adoption of the practice for decades.
This battle led to the emergence of "evidence based medicine." (Though Bloodletting remained in mainstream Medicine until 1923)
The increase in photon delay as they pass near a large mass such as our Sun. This test helps confirm General Relativity. There is a hypothesis that it is a source of Spectral-line Redshift.
Two very distinct ideas (Physical vs. Abstract) that can mean the same place --
1. A physical volume outside earth's atmosphere always containing photons and perhaps a few atoms of matter.
2. The abstract concept of volume typically used to geometrically define physical locations and characteristics in three physical dimensions typically Euclidean space. It is used with many coordinate systems, most commonly Cartesian which uses x, y and z. This can easily be considered an Inertial Reference Frame. Similar to Newton's Absolute Space and Relative Space.
Big Bang proponents often use these two mutually-exclusive and contradictory ideas interchangeably. Big Bang models are uniformly unclear about which of these two definitions are used for Expansion conjecture: physical space or abstract space? Whether one refers to expansion of a physical volume or the coordinate system itself is a critical distinction. The failure to define this key term is a primary reason Big Bang is not yet a scientific claim.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Space
Space, Closed
"A space of finite volume without a boundary."
Closed Space is a self-canceling phrase combining two otherwise legitimate ideas which directly contradict each other - with no physical explanation or evidence; an extreme conjecture. It is an excellent example of a violation of the second rule of a scientific hypothesis that it may not be "internally inconsistent."
(No direct experimental evidence)
The conjecture that space has curvature, either positive (emerging from Einstein's General Relativity equations) or negative (that has no claimed basis). Unstated is the necessary implication that if space is curved, it must have an edge. There may be math models, but there is no physical example of a complete negatively-curved object or universe.
This is an example of a mathematics idea that has no evidence of a corresponding physical reality.
The abstract concept of volume described by three physical dimensions. It helps us to understand positions, distances and angles typically by using the Cartesian coordinate system x, y, and z. Together they provide us with coordinate space.
(Hilbert space is a math extension of Euclidean space allowing vector algebra and calculus to address infinite dimensions.)
A term for a set of General Relativity mathematics models which combine time with the three dimensions of volume to simplify some physics models.
It might be easier to understand this math as "Gravity-Time" since it actually deals with a force (Gravity) and Space has no forces of its own.
Most science experiments separate phenomena to examine them individually. Space-Time and Grand Unification ideas do the opposite - they generalize by combining ideas.
Punctuations in the relatively smoother spectrum of an astronomical light source. Astronomical bodies such as stars and galaxies provide an apparently smooth spectrum of radiation.
Spectral lines are sharp increases (emission spikes) or decreases (absorption dips) in luminous power. Spectral lines are usually unique to a specific atom allowing these spikes of emission and absorption lines to be used to discern which elements exist in distant astrophysical phenomena.
Radiation spectrums are not really smooth and "clean" because every part of a spectrum, every wavelength in the spectrum is made by a specific atom releasing a photon that has a non-zero width spike. There are millions of different emission lines. They add up together to the spectrum we see.
Absorption lines are caused by the photons going through gas or plasma clouds. If a photon has gone through many neutral Hydrogen gas clouds it has a whole set of adjacent absorption lines called a "Lyman Alpha Forest."
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Spectralines
An allegory or metaphor for a physics model of complex natural phenomena that is laughably oversimplified far beyond credibility. Pokes fun at Theoretical Physics models that make stunningly large or sweeping assumptions likely making the model meaningless.
Astronomical objects / phenomena used to measure the largest distances. Cepheid Variable stars, type 1a Supernovas, and even Gamma Ray Bursts have been used as standard candles. Phenomena are only used when they can be shown to have fairly reliable characteristics - independent of distance and age. However, see "Margin of Error."
A concentration of galaxies; large groups of smaller galaxy groups. The Shapley Supercluster is the largest one we recognize situated about 600-650 million light years from us.
Faster than the speed of light. ( "c++" ;-)
Forbidden by Special Realtivity, yet several astrophysical phenomena, including Jets from Blazars, appear to be exceeding the light "speed limit," some almost ten times the speed of light. Big Bang's Expansion conjecture admits to exceeding light speed. Separately, Inflation claims to have exceeded the speed of light by many magnitudes. An astrophysicist who worked on the GPS satellite system provided evidence and rationale that gravity travels much faster than light.
Supernova Rise and Decay Curves
(Supernova is abbreviated as "SN")
Supernovas are star explosions which are among the brightest astronomical events, putting out as much energy as an entire galaxy. They only last for a couple of weeks and occur with a frequency of about once every hundred years per galaxy.
There are three types of Supernovae. Type 1a Supernovas are used for measuring sticks or "Standard Candles." The graph of visible light increase and decrease over the few weeks as a Supernova 1a explodes are curves used to estimate distances at the farthest visible reaches of our Universe. Comparing "close" and distant supernova curves gives us some (wildly conflicting) interpretations of cosmology.
Supernova lifespan appears to increase with distance indicating space is stretching / expanding.
A math tool to describe and handle a multidimensional field of points (like a magnetic field) through transformations such as during rotation or change of geometry. Composed of an array of numbers or functions that describe as many properties of each point in a physical system as you need.
The hypothesis that Spectral line Redshift is caused by photons of light / radiation losing energy (wavelengths grow) in a linear fashion while traveling for millions to billions of years through space and having experienced thousands to trillions of particle interactions with matter (plasma, gas and dust) along the way.
A roughly linear increase in Spectral line Redshift (as opposed to some other function e.g. square or cube) proportional to distance is observed, though there are credible reports that some redshift values occur as multiples of a set number - more often that expected.
There is abundant strong experimental evidence that Spectral line Redshift is caused by multiple phenomena other than recession velocity or Universe expansion including observations of: Binary stars with differing redshifts, and our own Sun's solar center to limb redshift.
This is the leading concept undermining galaxy recession, Universe expansion and Big Bang. Tired Light was originally proposed by Fritz Zwicky in 1929 and supported by Edwin Hubble.
Tired light criticism includes the claims that Radiation / Light --
- can not lose energy without scattering, and
- causing spectral line widening or broadening,
- making radio waves decay faster than visible light -
"none of which is observed."
Tired light researchers point out how light is well known to transit a transparent medium (e.g. perpendicularly transiting air, water and glass), slowed by the refractive index - without detectable scattering or spectral line broadening.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#TiredLight
Every measurement has some inaccuracy and almost all scientific research has some unknown information. There is nothing inherently wrong with uncertainty.
What is harmful is not acknowledging uncertainty, failing to reveal it, estimate it or explain its meaning.
"A measurement result is complete only when accompanied by a quantitative statement of its uncertainty. The uncertainty is required in order to decide if the result is adequate for its intended purpose and to ascertain if it is consistent with other similar results." -National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
There are at least Three Types of Uncertainty (5)
- "Phenomena Variability (or Process) Uncertainty" arises from natural variability of the phenomena. e.g. planets do not keep the same orbits.
- "Measurement or Observational Uncertainty" arises from measurement and sampling errors. For example repeatedly measuring a building height and comparing the data may show different results. (Phenomena Variability and Measurement Uncertainty are compound errors so must be multiplied to establish their total uncertainty.)
- "Model Uncertainty" reflects incomplete knowledge. For example ecological processes and galaxy forming processes are so complicated, have so many variables, that no one understands them fully and some variables are simply left out. This means the parameters for computer models are estimated from observed data leaving "estimation uncertainty."
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#Uncertainty
In everyday life and in non-critical science experiments most people are content to get measurements within a few percent. When something is off by 10 percent, that's generally considered significant or unacceptable.
Cosmology is a considerably less exact study or discipline. Most cosmology researchers are happy to get two measurements within the right magnitude (within ten fold). If the results are within a multiple of two from what was expected - its time for a champagne party.
Precision? When distances to distant phenomena were consistent to within 10 percent one cosmologist declared that we are in a new era of "Precision Cosmology." See Uncertainty.
Link directly to this definition -- http://www.CosmologyScience.com/glossary.htm#ErrorMargin
The hypothesis that there is a limit to knowledge or information about a particle's location or speed. Its actually an inverse relationship - the more precisely you can measure one (location or speed) - the less precisely you can know the other.
The Uncertainty Principle is not about a change in a physical entity such as energy or matter. For example Quantum or Vacuum Fluctuations concern physical changes - not limits to information.
Quantum mechanics depends on this principle and would "collapse" if this principle is invalidated.
(This is only amusingly related to the Hyper-Certainty Principle.)
Universe
Everything. All matter, forces, energy, space, and time.
It should be that simple, but there are several different size definitions. From largest to smallest:
Physical Universe = all matter, forces, energy and time we can understand using verifiable laws of physics.
Observable Universe is limited to the radius of what we see or detect with our strongest tools.
Big Bang Universe = all matter, forces, energy and time within the maximum distance reachable under the 14 billion year time limit of the Big Bang conjecture. Note: Under Big Bang the Observable Universe is smaller than under non-expanding, Static or infinite universes because Big Bang has a time before which light could not have been emitted.
Multi-verses: The conjecture of multiple Universes is an internally inconsistent claim, thus failing to meet the minimum threshold of having a scientific hypothesis, therefore it remains science fiction.Vacuum / Quantum Fluctuations, Virtual Particles
(No direct experimental evidence)
The conjecture that matter pops into and out of existence (in an untestably short amount of time - less than 10 to the minus 43rd of a second) without anything converted from or to energy. This violates the fundamental law of physics of energy and mass conservation ("but only for short times").
This conjecture is sometimes wrongly called "Theory of virtual particles" - when it is not a 'theory' or even a hypothesis.
Some interpret Casimir Effect and Lamb Shift as support for this conjecture.
Both Expanding Universe models, Big Bang and Steady-State, claim this effect, Static Universe models do not.
Verification and Falsifiability
Verification means a hypothesis can repeatedly pass a test - under explicit conditions. Verification is not the same as falsifiability. Falsifiability means a claim can fail a test.
Verification is one of the fundamental parts of modern science. Until it is tested and verified, a hypothesis is highly suspect. The origin and reason for a hypothesis is irrelevant or meaningless, the only thing that gives it real value is independent verification.
The next step is Falsifiability. Can the claim be shown to fail a test?
Voids or Bubbles (and Supervoids)
Large volumes of physical space with very few or no luminous galaxies. Voids do contain a significant percent of the universe's gas, plasma and dust The largest studied void is about 3.5 billion light years across.
A math tool to calculate the Kinetic Energy of a number of particles in a stable system.
Walls are Filaments (the largest structures) which are significantly (that's ambiguous) larger along their largest axis than their second largest axis. The largest reported is the "Sloan Great Wall" at about 1.4 Billion light years long.
References and Notes:
(1) "Humor" inspired by Tony Darnell atDeep Astronomy.com (He gets the credit, I get the blame.)
(2) "Principles of Physical Cosmology", Peebles, P.J.E., Princeton, 1993
(3) Hubble's Cosmology: From a Finite Expanding Universe to a Static Endless Universe", A. Assis et all, Astronomical Society of Pacific, 2009
(4) "Untrivial Redshifts: A Bibliographical Catalogue [of more than 700 unexplained redshift phenomena and events]", H. J. Reboul, Astronomy and Astrophysics Suppl., Vol. 45, pp. 129-144, 1981
(5)"Galactic Rotation Described by a Thin-Disk Gravitational Model Without Dark Matter", C. F. Gallo and James Q. Feng, Journal of Cosmology, April 2010, Vol 6, 1373-1380.
(5)"Proper Motions and Distances of Quasars," Y.P. Varshni (1980).
(6) Derived from an unpublished paper by John Williams of Davis California
Notes:
1. Many links provided here are to Wikipedia. (The journal Nature published a comparison of Wikipedia and Encyclopedia Britannica entries and found them to have very similar numbers and gravity of errors. Britannica disputes the methods used.) While no encyclopedia information is perfect, and Wikipedia has turned into a fairly reliable and consistent source of cosmology astrophysics information in the 2008-2009 era, I urge using Wikipedia references only as a "first cut"; an introduction and overview. For more detailed and accurate information I suggest reviewing the references listed at the end of the articles. Unfortunately, Wikipedia is not yet comprehensive or neutral. It has a strong pro-Big Bang bias which can be observed in many parts, but perhaps most clearly in how there is a "Criticism" section for Steady-State model article, but there is no similar 'Criticism' section allowed for the Big Bang article. What is arguably worse, its "Non-standard cosmology" article is almost wholly biased with Big Bang advocacy and the diminishment, rather than explanation, of Alternative Cosmology Models. Appallingly, Wikipedia has absolutely no mention of the previous cosmology "standard model" - the Open or Infinite Static Universe (as distinguished from Einstein's Closed Static Universe) as of this writing.
2. Professor Feynman's full quote "Now I'm going to discuss how we would look for a new Law. In general we look for a new Law by the following process. First we guess it. No, don't laugh, that is the real truth. Then we compute the consequences of the guess, to see what, if this law that we guessed is right, what it would imply. And then we compare those computation results to Nature; or we say compare to experiment or experience. Compare it directly to observation to see if it works. If it disagrees with experiment, it's wrong. In that simple statement is the key to science. It doesn't make a difference how beautiful your guess is, it doesn't make a difference how smart you are, or what your name is. If it disagrees with experiment, it's wrong. That's all there is to it."
This website and its contents are © Copyright 1999-2025 David j Dilworth.
All rights are reserved worldwide (and throughout our Milky Way Galaxy).
David Dilworth is one of only a handful of lifetime members of the organization Committee for Scientific Inquiry (formerly known as CSICOP).
David occasionally provides science repair services as a Quantum Mechanic ;-)
His 2009 paper "Ground Rules for Cosmological Physics" was published by the Astronomical Society of the Pacific in the 2008 Cosmology Conference "CCC2" Proceedings.
| Home | Overview | References | News | Blog |
– P.O. Box 100, Charmel, California 93921